When it comes to maintaining and repairing vehicles, one term you’ve likely heard time and time again is “OEM.” But what exactly does OEM mean, and why is it such a crucial factor in the world of auto parts?
In this article, we’ll break down what OEM is, why it matters, and how picking the right parts can make a big difference for your car’s performance and health.
1. What Does OEM Mean in Cars?
OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer, which refers to the car manufacturer that makes the parts used to build a vehicle.
Original equipment manufacturer parts are sourced directly from the factory that produced the original components, ensuring they meet the same quality standards, specifications, and performance as the parts originally used in your vehicle.

2. Why OEM Parts Are Important for Your Car?
Selecting the right parts is crucial for your vehicle’s performance and lifespan, making OEM parts a wise investment for car owners. Here’s why:
- Reliability and Durability
OEM parts are built to the highest standards, ensuring long-lasting reliability. Unlike aftermarket parts, which can vary in quality, OEM components match the lifespan of your car’s original parts, ensuring smooth, trouble-free performance on any drive. - Perfect Fit and Functionality
OEM parts are designed to fit your vehicle perfectly, eliminating concerns about compatibility or adjustments. They are fully compatible with your car’s systems, integrating seamlessly to maintain the same level of performance as when it left the factory. - Safety and Performance
OEM parts play a crucial role in maintaining vehicle safety. Components like brakes, airbags, and engine parts meet strict safety standards, helping reduce the risk of malfunctions or accidents. High-quality materials also preserve fuel efficiency and smooth driving. - Resale Value
Investing in OEM parts helps maintain your car’s resale value. Vehicles with OEM components are seen as well-maintained and authentic, making them more attractive to potential buyers.

3. OEM vs. Aftermarket Parts: What’s the Difference?
In car repairs and replacements, there are typically two primary options: OEM parts and aftermarket parts.
Aftermarket parts are made by third-party manufacturers and are designed to fit a range of makes and models, though they’re not exact replicas of the original components.
For instance, aftermarket brake pads, air filters, and exhaust systems may perform similarly to OEM parts, but the quality, fit, and performance can vary depending on the manufacturer.
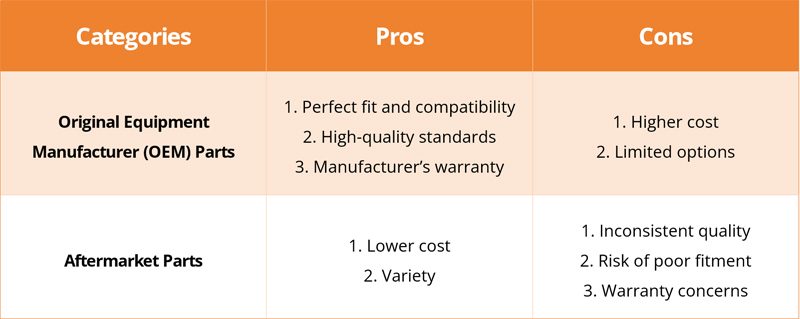
Key Differences Between OEM and Aftermarket Parts
- Cost: Aftermarket replacement parts are usually cheaper than original equipment manufacturer parts, making them a good choice for budget-conscious repairs. However, this often comes with trade-offs in quality and longevity.
- Quality: OEM parts are the benchmark, crafted to match the exact specifications of the original parts. Aftermarket parts can vary widely in quality, with some matching OEM standards and others falling short.
- Warranty: OEM parts typically come with a warranty for peace of mind. While aftermarket parts may offer warranties, they can vary significantly and may not provide the same level of coverage.
- Fitment: OEM parts are guaranteed to fit your vehicle exactly as the originals. Aftermarket parts may not always fit perfectly and could require adjustments or have compatibility issues.
Pros and Cons of OEM vs. Aftermarket Parts
Common Myths About OEM Parts Debunked
- Myth: OEM parts are always more expensive than aftermarket parts. While OEM parts may be more expensive in some cases, the price difference is often minimal when you consider the long-term value and reliability they provide.
- Myth: Aftermarket parts are always bad quality. While some aftermarket parts are subpar, many reputable manufacturers produce high-quality aftermarket components that perform on par with, or even outperform, OEM products.
- Myth: OEM parts are identical to the parts originally installed in the vehicle. While OEM parts are made to the same specifications, there may be slight variations depending on production runs or model years. However, these differences rarely affect the part’s performance.
4. Are OEM Parts Worth the Extra Cost?
A common question in car repairs is whether the higher cost of original equipment manufacturer parts is justified compared to aftermarket alternatives. While OEM parts tend to be more expensive, they can often prove to be a more economical choice in the long run, depending on several key factors.

How to Assess the Value of OEM Parts
When deciding whether to choose OEM, consider your vehicle’s type, age, and usage:
- Vehicle Type: For luxury or high-performance vehicles, OEM parts are essential for maintaining precision and value. For everyday cars, aftermarket parts may be fine, but OEM provides added peace of mind.
- Vehicle Age: Older vehicles may seem like a good candidate for cheaper aftermarket parts, but OEM parts help maintain performance and prevent issues from incompatible components.
- Usage: For heavy-duty use (towing, off-roading, etc.), investing in OEM parts ensures durability and reliability under stress, where aftermarket parts might fall short.
Real-Life Scenarios for Choosing OEM
- Engine and Transmission Repairs: For major repairs, using OEM parts is crucial to avoid further damage and ensure the vehicle runs as intended.
- Safety Features: Components like airbags and brakes are critical for safety. OEM parts ensure these systems meet the necessary standards.
- Resale Value: Vehicles with OEM parts are more attractive to buyers, especially those who value quality and reliability, helping preserve resale value.
5. How to Identify OEM Parts for Your Vehicle?
Replacing auto parts requires ensuring you’re getting authentic original equipment manufacturer parts to preserve your vehicle’s performance and reliability. Although identifying OEM parts can be tricky, it’s much easier with the right knowledge.

Tips for Identifying OEM Parts
- Check the Manufacturer’s Website: The best way to confirm a part is OEM is by visiting the manufacturer’s website or checking the vehicle’s manual. They usually list part numbers and specs for your vehicle.
- Look for Packaging and Documentation: OEM parts typically come in branded packaging with the manufacturer’s logo. Be cautious of parts in plain or generic packaging.
- Ask for Part Numbers: Every OEM part has a unique part number. Ask the seller for the part number and verify it on the manufacturer’s website to confirm authenticity.
The Importance of Part Numbers and Labels
Part numbers are the most reliable way to verify a part’s authenticity. Each OEM part has a unique number that matches the specific design and fit for your vehicle. Some OEM parts also include labels or barcodes that can be cross-checked for authenticity.
Work with Authorized Dealers
To ensure you’re getting genuine car parts, buy from authorized dealers or certified suppliers. These dealers work directly with the original manufacturer and are more likely to carry OEM parts. Authorized service centers are also a safe choice for repairs. Avoid unverified third-party sellers who can’t guarantee authenticity.

6. Common FAQs About OEM in the Automotive Industry
Q: What’s the difference between OEM and ODM?
A: OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer, referring to products or parts made based on another company’s designs and specifications. These parts are typically sold under the brand name of the company that created the specifications.
ODM stands for Original Design Manufacturer, which designs and manufactures products that are sold under another company’s brand. The company purchasing ODM products generally has less control over the design since the ODM handles both design and production.
Q: Can I use OEM parts in a used or older car?
A: Yes, OEM parts are perfect for older cars. They help maintain the vehicle’s original performance, safety, and reliability, preserving its longevity and value. For critical components like the engine or transmission, OEM parts are especially important for keeping your car in top condition.

Q: Do OEM parts affect my car’s resale value?
A: Yes, using OEM parts can help maintain or even increase your vehicle’s resale value. Buyers tend to prefer cars with OEM parts because they indicate the vehicle has been properly maintained and retains its original specifications. This can enhance trust and reliability, making your car more appealing to potential buyers.
Q: Are OEM parts covered by warranty?
A: Yes, OEM parts usually come with a warranty that guarantees they’re free from defects and function as expected. The warranty is often similar to the manufacturer’s original vehicle warranty, offering peace of mind. Always check specific warranty details with the seller.
Q: How do I know if a part is OEM or aftermarket?
A: To verify if a part is OEM or aftermarket:
- Check the part number: Cross-reference it with the manufacturer’s catalog.
- Examine the packaging: OEM parts come in branded packaging, while aftermarket parts often don’t.
- Ask the seller: Reputable sellers will confirm if a part is OEM.
- Authorized dealerships: Purchasing from an authorized dealer or service center ensures you’re getting OEM parts.
7. Conclusion
OEM parts are considered the gold standard in the auto repair industry. Made by the same factory as your vehicle’s original components, OEM parts ensure perfect fit, reliability, and long-lasting performance.
While they may cost more upfront, they often save you money in the long run by reducing the need for frequent replacements and ensuring your car stays in top condition.

At Woda, we provide top-quality OEM automotive engine parts designed to keep your vehicle running smoothly. If you’re looking for a reliable auto parts supplier, feel free to contact us anytime to discover how our expert solutions can help maintain your car’s performance and value.