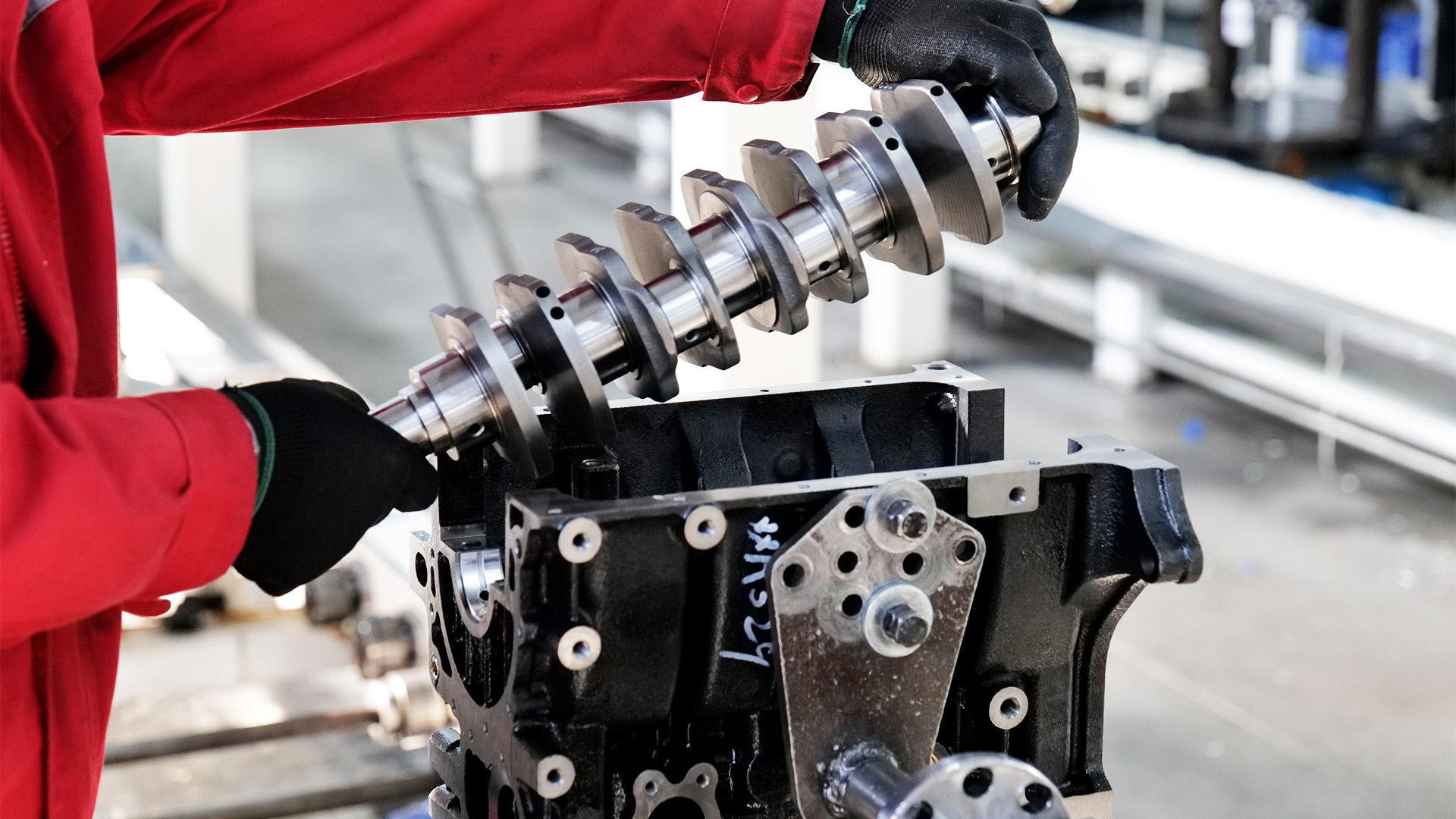
When it comes to sourcing auto parts, understanding engine specifications isn’t just for engineers—it’s a must for B2B buyers, distributors, and auto parts professionals.
A single mismatch in displacement, torque, or material can lead to costly returns, customer dissatisfaction, and even engine failures. That’s why knowing what engine specifications mean—and how to apply them to parts procurement—is crucial for staying competitive in today’s global auto parts market.
In this article, we’ll break down the key engine specifications every auto parts buyer should know, explain how these parameters impact parts selection, and show you a real-world case study using the KA24 engine.

Key Engine Specifications You Should Know
1. Engine Displacement
Displacement refers to the total volume that all the pistons in an engine move through, typically measured in liters (L) or cubic centimeters (cc).
This figure directly affects engine size, power potential, and component sizing.
🔧 Why it matters:
A 2.4L engine and a 3.0L engine might appear similar externally, but the internal components—such as pistons, cylinder heads, and gaskets—can be entirely different. Selecting the wrong parts can cause incompatibility, poor performance, or engine failure.
2. Bore and Stroke
Bore is the diameter of the engine’s cylinders, while stroke is the distance the piston travels inside the cylinder. Together, they shape the engine’s performance profile.
🔧 Why it matters:
Engines with a short stroke often generate higher RPM and horsepower, while a long stroke delivers better torque at lower speeds.
These dimensions influence key components like pistons, crankshafts, and cylinder block design, and must match exactly for proper engine function.

3. Compression Ratio
The compression ratio indicates the degree to which the engine compresses the air-fuel mixture prior to combustion. It’s a key factor in engine efficiency and combustion characteristics.
🔧 Why it matters:
Gasoline engines typically operate between 8:1 to 12:1, while diesel engines require much higher ratios, often 14:1 to 22:1.
Using the wrong parts in high-compression engines can result in knocking, overheating, or premature component failure.
4. Horsepower and Torque
Horsepower measures the engine’s total power output, while torque reflects the rotational force the engine produces.
🔧 Why it matters:
These specs offer insight into the stress levels that engine parts endure. Engines producing high torque demand stronger crankshafts, connecting rods, and clutches, as well as enhanced cooling and sealing systems.
5. Fuel Type and Engine Configuration
The fuel type—gasoline or diesel—and engine configuration—inline, V-type, or flat—determine the engine’s basic design and its component requirements.
🔧 Why it matters:
These factors influence everything from combustion methods and compression ratios to ignition systems and cylinder head designs. An inline-4 gasoline engine requires different parts than a V6 diesel, even if their displacements are similar.

6. Valves per Cylinder
The number of valves per cylinder—commonly 2, 3, 4, or even 5—determines how air and exhaust flow through the engine.
🔧 Why it matters:
More valves improve airflow and efficiency but require more complex camshafts, timing components, and valvetrain parts.
Failing to match the correct components can lead to poor performance or engine damage.
7. Fuel Injection System Type
Modern engines use various fuel injection methods, including port injection, direct injection, and common rail systems.
🔧 Why it matters:
Each system requires specific injectors, fuel pumps, and cylinder head designs. Using mismatched components can result in fuel delivery issues and engine inefficiency.
8. Induction System
Engines can be naturally aspirated, turbocharged, or supercharged, depending on how they draw in air.
🔧 Why it matters:
Forced induction engines operate under higher pressure and heat, requiring reinforced pistons, gaskets, and upgraded cooling systems to withstand the added stress.

9. Emission Standards Compliance
Engines are designed to meet specific emissions standards such as Euro 6 or EPA Tier 4, which affects the integration of systems like EGR, DPF, and SCR.
🔧 Why it matters:
Non-compliant parts can cause legal, performance, and compatibility issues, especially in export markets or regulated regions.
10. Engine Materials
Engine blocks and heads are commonly made of cast iron, aluminum, or compacted graphite iron (CGI).
🔧 Why it matters:
Different materials expand at different rates and require gaskets and seals designed for those materials.
Incorrect part selection can cause leaks, warping, or early failure.
11. Engine Weight and Mounting
Engine weight affects not only vehicle balance but also mounting systems and cooling requirements.
🔧 Why it matters:
Using incorrect brackets or supports can lead to vibration issues, structural stress, and even damage to adjacent systems.

12. Lubrication System Specs
Engine lubrication involves specific oil types, capacities, and service intervals, all critical for optimal performance.
🔧 Why it matters:
Using the wrong oil pump, filter, or even oil type can cause poor lubrication, overheating, and reduced engine life.
B2B buyers should always verify oil-related specs when supplying maintenance kits or parts.
13. Cooling System Type
Engines may be air-cooled or water-cooled, with specific system designs.
🔧 Why it matters:
Selecting the wrong radiators, water pumps, thermostats, or hoses can cause overheating, leaks, or engine failure.
14. Estimated Engine Lifespan
Engine lifespan, often measured in kilometers or hours of operation, signals how durable the engine is designed to be.
🔧 Why it matters:
This influences parts selection for heavy-duty, premium, or economy segments, particularly for fleets, industrial engines, or export buyers.

Real-World Case Study: KA24 Engine Specifications
To illustrate how these engine specifications come together in practice, let’s take a look at the KA24 engine, a popular 2.4L inline-4 gasoline engine widely used in Nissan vehicles.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Engine Code | KA24 |
| Configuration | Inline 4-cylinder |
| Displacement | 2389 cc (2.4L) |
| Cylinder Bore | 89 mm |
| Piston Stroke | 96 mm |
| Compression Ratio | 9.2 – 9.5 |
| Valves per Cylinder | 4 |
| Fuel System | Injector-based (EFI) |
| Induction System | Naturally Aspirated |
| Power Output | 140 – 155 hp |
| Torque Output | 200 – 215 Nm |
| Fuel Type | Petrol |
| Block Material | Cast Iron |
| Engine Weight | Approx. 170 kg |
| Recommended Oil Grades | 5W-30 / 5W-40 / 10W-30 / 10W-40 |
| Oil Capacity | 4.1 liters |
| Oil Change Interval | 15,000 km |
| Estimated Lifespan | Approx. 350,000 km |
🔧 Why this matters for B2B buyers:
The KA24 engine showcases why understanding detailed specs is critical for parts sourcing.
Differences in bore, stroke, compression ratio, and fuel system must be considered when sourcing pistons, cylinder heads, injectors, or gaskets.
Additionally, regional variants of the KA24 exist, making it essential to always cross-check full specs—not just the engine code—before placing orders.
At Nanjing Woda Auto Technology Co., Ltd., we help our customers avoid costly sourcing errors by providing full technical support and cross-checking engine data against our parts catalog.

Conclusion
For B2B buyers in the auto parts industry, understanding engine specifications is not optional—it’s essential. Knowing these key parameters ensures you source the right parts, reduce costly mistakes, and build long-term trust with your customers.
Need help verifying engine specs or sourcing compatible parts?
At Nanjing Woda Auto Technology Co., Ltd., we offer professional support and a complete catalog of engine components for both diesel and gasoline engines.
Contact our team today or visit autopartswd.com to explore our products and request a quote.