Ever wondered what really powers your car beyond just turning the key? To truly understand how a car engine works, it’s essential to know the parts that keep it running.
Whether you’re a student, a mechanic, a curious car owner, or a parts supplier, this A to Z guide breaks down the most important engine components in a way that’s practical, clear, and easy to remember.
A – Air Filter
The air filter serves as the engine’s first line of defense, keeping out dust, dirt, and other airborne particles from the intake system.
By ensuring a clean, consistent flow of air to the combustion chamber, it helps maintain optimal performance and fuel efficiency. When clogged, it can restrict airflow and reduce engine power.

B – Battery
Though it sits outside the engine, the battery is essential. It stores electrical energy and delivers the initial power needed to start the engine and activate key systems like ignition and fuel injection.
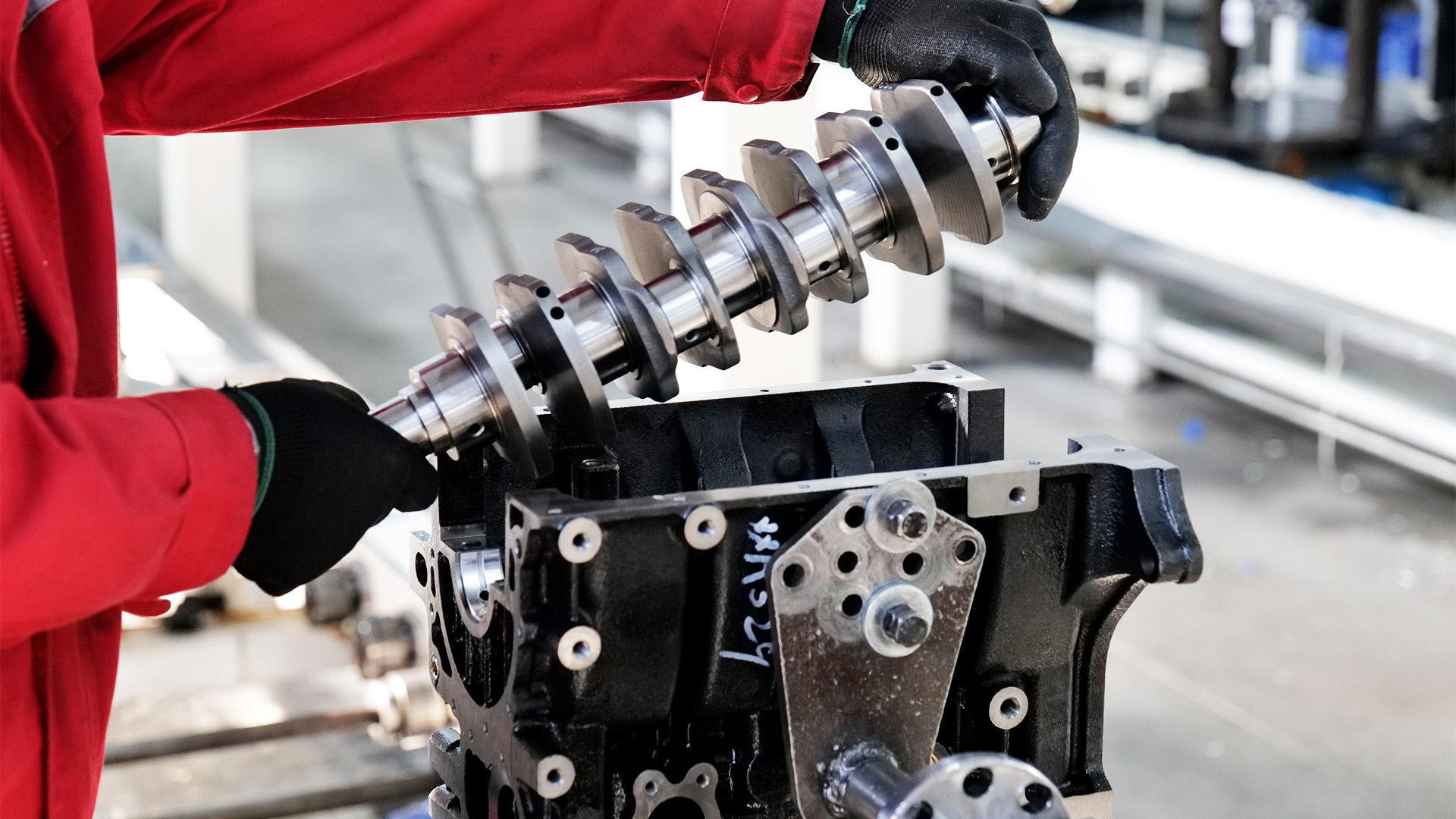
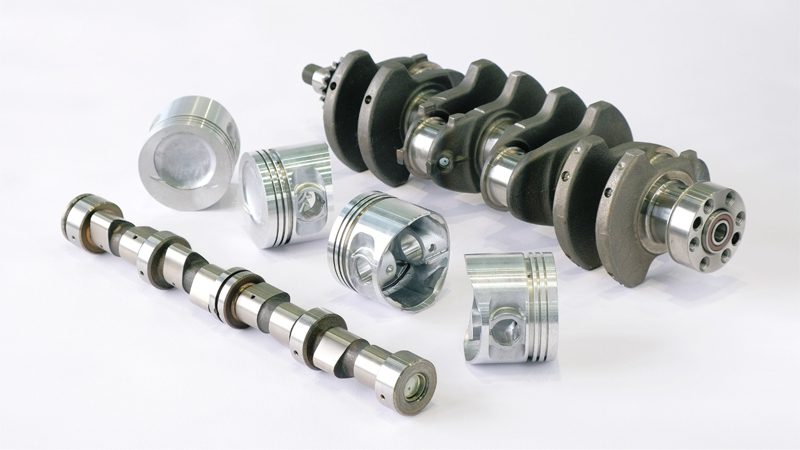
C – Camshaft & Crankshaft
The camshaft is responsible for the precise timing of valve operations, opening and closing the intake and exhaust valves in sync with the pistons. It must endure high rotational speeds and maintain exact alignment with the crankshaft to ensure efficient combustion.
The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational force that drives the wheels. It’s one of the most heavily stressed parts in the engine, designed for strength, balance, and long-term reliability.

D – Distributor
Used in older engines, the distributor sends high-voltage electricity from the ignition coil to the spark plugs in the correct firing order. Though many modern engines no longer use them, they’re still important to understand.
E – Engine Block
This is the engine’s foundation. It houses the cylinders, crankshaft, oil galleries, and coolant passages. Everything bolts onto it—making it a critical piece of the puzzle.
F – Fuel Injector
Fuel injectors spray precise amounts of fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber. They replaced carburetors in most modern vehicles for better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
G – Gasket
Gaskets are the unsung heroes that seal joints between metal engine parts, keeping oil, coolant, and gases where they belong. Without them, engines would leak and fail.
H – Head (Cylinder Head)
The cylinder head plays a critical role in engine efficiency and reliability. It seals the top of the combustion chamber, houses key components like intake/exhaust valves, and provides passages for fuel-air mixture and exhaust flow.
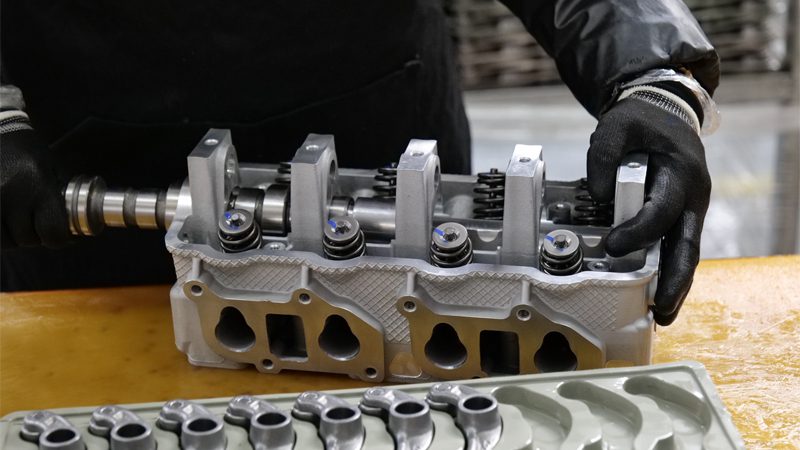

I – Ignition Coil
The ignition coil amplifies the battery’s low voltage into a powerful surge strong enough to ignite the spark plugs. It’s a crucial part of the ignition system—without it, there’s no spark, and the engine won’t run.
J – Jet (Carburetor Jet)
In older engines with carburetors, jets control fuel flow into the air stream. They may seem old-school now, but they’re still relevant in small motors and classic cars.
K – Knock Sensor
This sensor detects abnormal engine noises (knocking or pinging) and tells the ECU to adjust timing, helping prevent serious engine damage.
L – Lifters (Tappets)
Lifters sit between the camshaft and valves, transferring motion to open and close the valves. Hydraulic lifters also help reduce engine noise and wear.
M – Manifold (Intake/Exhaust)
The intake manifold delivers air (or air-fuel mixture) to the engine, while the exhaust manifold collects spent gases and routes them to the exhaust system. Both are essential for engine breathing.
N – Neutral Safety Switch
This small but important safety feature prevents the engine from starting unless the car is in park or neutral—reducing the chance of accidental movement.
O – Oil Pump
The oil pump is essential for engine lubrication, ensuring oil reaches critical components like the crankshaft, camshaft, and valve train. A failure in this part can quickly lead to severe engine damage. It must maintain stable oil pressure and operate efficiently under all engine loads.
P – Piston
Pistons compress the air-fuel mix and absorb the force of combustion, transferring it to the crankshaft. They endure high pressure and temperature every time your engine fires.

Q – Quick Connect Fuel Line
Quick connect fuel lines simplify maintenance by allowing you to attach or detach fuel hoses swiftly and securely—no tools required. They’re a modern convenience that saves time during repairs or replacements.
R – Radiator
The radiator keeps the engine cool by transferring heat from the coolant to the outside air. Without it, overheating would be a constant issue.
S – Spark Plug
Spark plugs create the explosion that drives your engine. They’re small, but their role in combustion is absolutely critical.
T – Timing Belt & Timing Chain
The timing belt synchronizes the rotation of the camshaft and crankshaft, ensuring the valves open and close precisely in step with the pistons. Made of reinforced rubber, it requires regular replacement—if it breaks, it can cause serious engine damage.
Some engines use a timing chain instead, which is made of metal and typically lasts much longer. While more durable, timing chains can still wear over time and may require tensioner or guide replacement to maintain proper function.

U – Universal Joint (U-joint)
U-joints allow flexibility in the drivetrain, helping transfer power even as the vehicle’s angles shift during motion.
V – Valve
Valves regulate airflow and exhaust within the combustion chamber. Their precise operation ensures efficiency and power.
W – Water Pump
This pump keeps coolant moving through the engine to prevent overheating. It’s typically belt-driven and essential for thermal regulation.
X – X-Member (Crossmember)
The crossmember provides structural support for the engine and transmission. It’s especially important in larger or high-performance vehicles.
Y – Y-Pipe
Used in dual exhaust systems, the Y-pipe merges gas flow into a single stream, improving efficiency and simplifying design.
Z – Zero Emission Components
In electric and hybrid vehicles, zero-emission systems replace traditional engine parts. Even in gasoline engines, systems like EGR valves and catalytic converters work to lower pollution.
Conclusion
And there you have it—your A to Z guide to essential car engine parts. Whether you’re diagnosing engine problems, exploring auto parts for business, or just brushing up your knowledge, understanding these components gives you an edge.
About Us
At Nanjing Woda Auto Technology Co., Ltd, we take pride in producing top-quality engine parts, including camshafts, crankshafts, cylinder heads, oil pumps, turbochargers, and more. Our parts power vehicles in over 100 countries, backed by reliable engineering and global distribution.
Need dependable and affordable engine components? Contact us today to explore tailored business solutions and volume discounts.