The engine is the very heart of every motor vehicle, driving motion and power through precise combustion and efficient exhaust flow management. However, the car valve—often the unsung hero—regulates air and fuel flow, ensuring each combustion cycle stays perfectly balanced at all times.
Ever wondered what keeps your car engine running smoothly? It all starts with the humble valves in the engine. Today, we’ll explain what these do, how they fail, and how understanding them can help you keep your car running for many years to come.
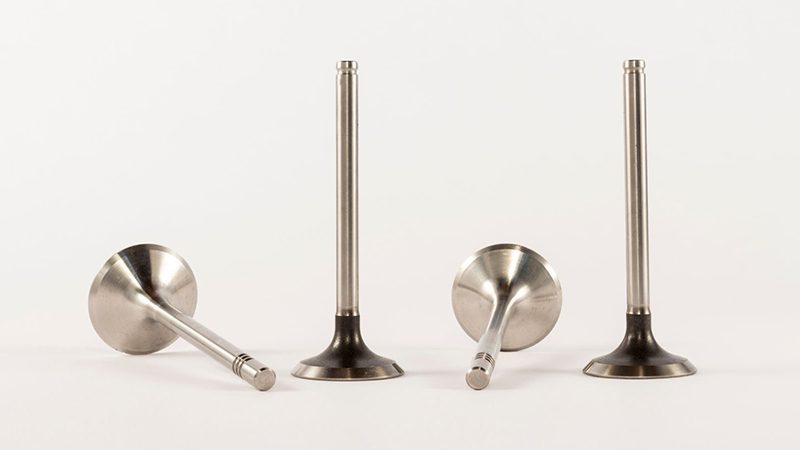

What is an Engine Valve and How Does it Operate?
Engine valves regulate the mixture of fuel, air, exhaust gases, and fumes in the engine’s combustion chamber. They are timed precisely to open and close at exact intervals, keeping the engine efficient so that little fuel is wasted.
Engine valves are positioned above the engine’s combustion chamber, nestled within the part of the engine known as the cylinder head. They work in conjunction with the camshaft that controls them, the intake valves that allow the air-fuel mixture to enter, and the exhaust valves that release the burned mixture exhaust gases after a successful combustion chamber cycle.
The concept of an engine valve traces its roots back to the 19th century when it evolved from an antiquated poppet valve. Continual advances in the 20th century, the invention of overhead camshafts, and variable valve timing (VVT) all helped the valve mechanism progress and thus made the system what it is today.
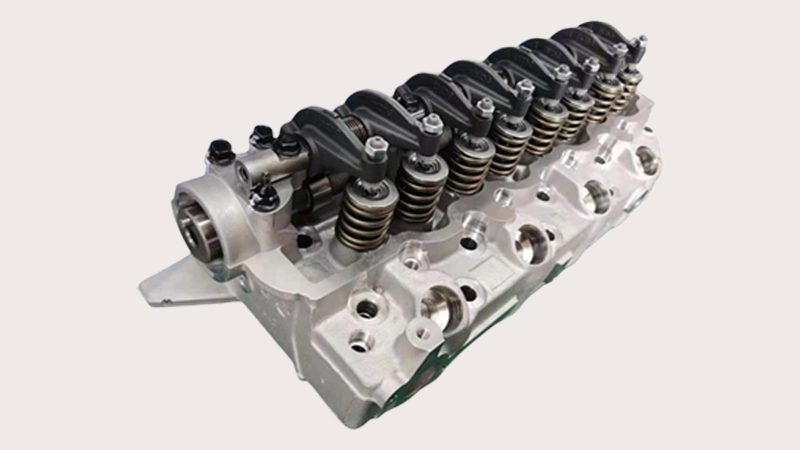

Intake vs. Exhaust Valves: Understanding Their Key Functions
The combustion process kicks off with the intake valve opening at precisely the right time to let in fuel and air into the valve engine’s chamber. As the engine’s piston moves upward and compresses the mixture, the intake valves close shut to seal the exhaust system and chamber.
Next, the spark plug ignites the compressed mixture creating a powerful explosion which, once again, pushes the piston downward. Once this explosion is complete, an exhaust valve also opens on time to expel exhaust gasses out of the chamber and make fresh air in the chamber ready for the next cycle.

This process is repeated time and time again and is essentially what are valves in an engine designed to do. The key to this process lies in the precisely timed opening and closing sequences of both the intake valve and exhaust valve.
Without such precise timing, the valve engine wouldn’t generate as much power from the same amount of air and fuel, nor would it achieve comparable levels of fuel efficiency. This is essentially “what do car engine valves do“, but to understand them more thoroughly, we need to know what makes an engine valve tick.
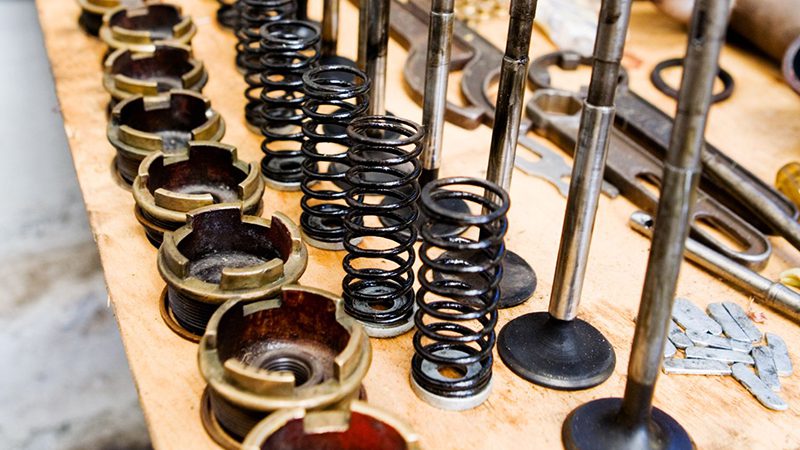
Anatomy of an Engine Valve: Key Components Explained
With all of the essentials in mind, now it’s time to dissect the car valve and see what are valves in an engine are made out of.

What is a Valve Head?
The valve head is tasked with ensuring maximum efficiency by sealing the chamber once the piston moves to its upward position thus stopping exhaust gases from exiting the chamber.
What is a Valve Stem?
Among all the components of valves in engine designs, the valve stem ensures consistently controlled movement. Attached to the valve head, the valve stem guides the movement of the valve and thus the valve guide ensures the valve train always moves with perfect precision and timing.
What is a Valve Spring?
Designed to support the valve stem, the valve spring returns the valve to its original closed position in sync with the downward motion of the cylinder head and the piston, ensuring exhaust gases are effectively pushed out through the exhaust valve.
What is a Valve Seat?
Finally, the valve seat, as the name might suggest, functions as a cushion for the valve to seal against as it ensures an airtight fit which also helps to reduce wear and tear.

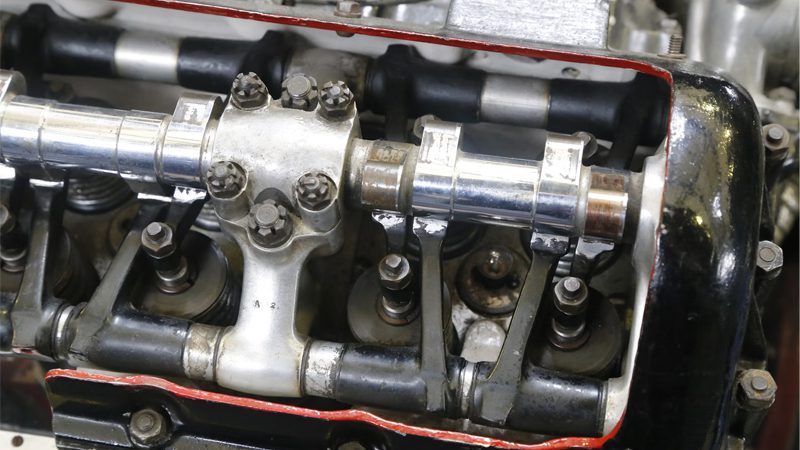
The 4 Cycles of Engine Valve Operation
The valve engine operation cycle consists of four distinct stages: the intake stroke, the compression stroke, the combustion stroke, and the exhaust stroke. The reason why they are called strokes is because they refer to the movement of the piston within the engine cylinder at every stage of the cycle.
It’s also important to note that the precise synchronization of the intake and exhaust valves is controlled by the engine’s crankshaft itself, which usually drives a belt or a timing chain. This system acts as the glue that holds the entire engine cycle together.
1. Intake Stroke
During a process known as the intake stroke, the intake valve opens while the piston moves downward. This kicks off the first process of the combustion cycle where a vacuum is created by the piston which pushes the air and fuel mixture in.
2. Compression Stroke
Once the air and fuel make their way through the intake manifold into the chamber, the compression stroke begins with the intake valve closing as the piston begins its upward trajectory. This traps the mixture at the top of the chamber and primes it for ignition.
3. Combustion Stroke
This is where all the power is being made as the compressed air and fuel mixture gets ignited via a spark plug during a combustion stroke. This ignition pushes the piston down and that’s what is being transferred to the wheels as motion power.
4. Exhaust Stroke
The cycle closes with the piston moving up once again, opening the exhaust valves. This lets out the burnt exhaust gases, which is crucial before starting the next cycle. The chamber needs to be exhausted, which is why this part of the process is known as the exhaust stroke.

A Guide to Understanding Poppet, Reed, and Rotary Valves
Poppet Valves
The poppet valve is what we find in most cars today, giving us a clearer picture of what are valves in an engine and their role in high-pressure systems. Poppet car valves are commonly found in four-stroke engines due to their mushroom-like design which helps with high pressures usually associated with four-stroke engines.
Rotary Valves
Rotary valves are often viewed as an alternative to poppet valves but aren’t nearly as common in modern auto engines. They operate by rotating consistently to control the flow of air and fuel, which produces less mechanical noise. Be that as it may, they generally aren’t as reliable as poppet car valves which makes the maintenance process a bit more delicate.
Reed Valves
Reed valves are predominantly used in motorcycles and outboard motorboats because they are designed for two-stroke engines. They are lighter and extremely efficient for high-speed operations but aren’t as dependable for larger, more complex engines.
5 Key Differences Between Poppet, Reed, and Rotary Valves
| Feature | Poppet Valves | Rotary Valves | Reed Valves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Usage | Standard in four-stroke engines | Limited to specific designs (aircraft/racing) | Common in two-stroke engines |
| Operation | Opens/closes via camshaft | Opens/closes by rotating | Opens/closes based on pressure |
| Complexity | Simple and reliable | More complex, harder to maintain | Very simple, lightweight |
| Efficiency | High efficiency and durability | Smooth operation, less noise | Efficient for high-speed use |
| Applications | Cars, trucks, general vehicles | Experimental, high-performance engines | Motorcycles, small engines |
Common Issues with Engine Valves
Now it’s time to go in-depth about what common issues one can expect with engine car valves. We’ll go over all of the associated symptoms these valve systems face, what causes them, and how one can mitigate these through timely maintenance.

Top 6 Signs Your Engine Valves Need Attention
There are quite a few potential symptoms to look out for, but the most common ones are:
- Engine Misfiring – This is usually the most common symptom to look out for and is characterized by a cylinder being unable to ignite the air-fuel mixture properly.
- Loss of Engine Performance – As the engine fails to utilize maximum combustion chamber potential, it struggles to deliver optimal engine power and thus can feel sluggish.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency – Engine valve problems tend to disrupt the optimal delivery of fuel into the engine which can lead to higher-than-usual MPG numbers.
- Rough Idle – The engine can also shake or vibrate abnormally when idling due to the combustion chamber not being consistently utilized after each cycle.
- Unusual Noises – Popping, sputtering, or backfiring sounds tend to accompany valves in engine trouble, especially during engine misfiring.
- Excessive Smoking – Excessive white or black smoking from the exhaust can indicate problems with inefficient combustion or the exhaust valves opening too early/late.

5 Common Causes of Engine Valve Problems
Several factors can lead to valve problems over time, and these are the most common ones to look out for:
- Carbon Buildup – Direct injection engines are mostly affected by this problem when excess oil sludge deposits form on the valves and seats which can affect their closing and opening sequences.
- Overheating – Even though valves are designed to withstand high temperatures, they can sometimes warp or crack due to excessive heat. This is mostly associated with exhaust valves which endure high temperatures the most.
- Valve Timing Issues – If a camshaft, or its chain/belt experiences problems, it can lead to improper valve operation as these mechanisms are designed to control how and when valves open and close.
- Improper Maintenance – Engines require maintenance to operate at an optimal level, and if one neglects oil changes or uses low-quality oil/filters, it can lead to poor lubrication and problems with the valves.
- Wear and Tear – Time can also be an enemy as valve seats, stems, and guides slowly deteriorate over time and sadly can’t last forever.

Engine Valve Maintenance: Best Practices
To maximize the lifespan of your valve engine systems and to maintain optimal performance, be sure to consider the following basic maintenance tips:
- Use Premium Fuel – High-quality fuel aids in both cleaning the engine and stopping excessive carbon buildup, both of which will benefit your valves going forward.
- Change Oil Regularly – Oil is tasked with lubricating, cleaning, and cooling your valves, courtesy of the oil pump. If it’s not changed regularly, it will likely lose these essential properties.
- Inspect Your Cooling – Be sure to check your cooling system for leaks, bad seals, or low fluid levels as that can cause overheating and literally cook your car’s valves.
- Adjust Your Valves – Some engine valves require proper valve-clearing adjustments over time, so be sure to do your homework and adjust them when necessary.
- Use Additives if Recommended – Some engines also require/benefit from high-quality fuel system cleaners which can clear carbon deposits and extend the lifespan of your engine valves.
- Check for Irregularities – Being proactive and well-informed is the most important tip to keeping your engine safe, so be sure you know how to indicate these problems early, so you can solve them before they cause serious damage.

3 Key Advances in Valve Technology You Should Know
Consistent breakthroughs in metalworking, technology, and valve engine block manufacturing throughout the 20th and 21st centuries also brought various advances in engine valve technology, these are the ones making the most noticeable impact.
Variable Valve Timing (VVT) Systems
Variable Valve Timing (VVT) systems rely on the engine speed and load to always make little adjustments and further increase efficiency and power output. For example, VVT systems are used to make more power when the engine operates at higher RPMs while also maximizing efficiency when cruising or driving slowly.
Popular VVT systems include Honda’s legendary V-Tec, Toyota’s VVT-i, and BMW’s VANOS system, all of which aim to provide better performance, reduced emissions, and smoother operation across various driving conditions.

Innovations in Valve Materials
Modern-day materials and metalworking also provide tangible benefits to engine valve technology via solutions such as titanium or sodium-filled valve stems.
Titanium not only reduces the overall weight of the system and handles stress effectively in high-performance engines, but it also resists corrosion. This further increases the durability and lifespan of engine components under heavy load.
On the other hand, sodium-filled valve stems are known for their superior heat dissipation, making them ideal for forced-induction engines, especially when turbochargers are placed directly within the V of a V-engine, something usually associated with premium German performance cars.
Electric and Pneumatic Valve Systems
Electric and pneumatic valve systems, such as those in Koenigsegg’s amazing Freevalve technology, eliminate the need for a traditional rotating camshaft. With completely independent valve opening and closing sequences, electric and pneumatic valve systems represent vast potential for future applications.
FAQs
1. What is the function of engine valves?
Engine valves control the flow of air-fuel mixture into the combustion chamber and the release of exhaust gases after combustion. There are two main types:
- Intake valves allow the air-fuel mixture to enter the cylinder.
- Exhaust valves release burnt gases after combustion.
They play a vital role in engine breathing, performance, and fuel efficiency.
2. What are the symptoms of engine valve problems?
Common signs of engine valve issues include:
- Rough idling or engine misfires
- Loss of power or poor acceleration
- Excessive oil consumption or blue smoke from the exhaust
- Unusual tapping or ticking noises
These symptoms often indicate valve wear, leakage, or damage.
3. What happens when your valves go bad?
When engine valves fail, they may not seal properly. This leads to:
- Compression loss
- Poor engine performance
- Overheating or engine knocking
In severe cases, a broken valve can cause internal engine damage, including piston and cylinder head damage.
4. Can you run an engine with a bad valve?
Technically, yes—but it’s not recommended. Running an engine with a bad valve can lead to:
- Reduced fuel economy and power
- Further damage to pistons, spark plugs, or the catalytic converter
- Complete engine failure if left unchecked
It’s best to repair valve issues promptly to avoid costly repairs.
5. How much does it cost to replace engine valves?
The cost to replace engine valves can vary widely depending on:
- The type of vehicle
- Labor costs in your region
- Whether you’re replacing a single valve or doing a full valve job
On average, valve replacement can cost between $300 and $1,500. High-performance engines or extensive damage may increase the total cost.
Wrapping Up: The Heartbeat of Your Engine
By this point, we’ve covered almost everything there is to know about engine valves and what valves are responsible for in an engine. They are an essential aspect of the very thing that makes our cars what they are today.
From the early days of poppet valves to the amazing VVT and electric and pneumatic systems of today, engine valves are the gatekeepers of the internal combustion engine.
With 25 years of dedicated experience, Nanjing Woda Auto Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in high-quality OEM and aftermarket engine parts for all types of engines. Trusted by customers in over 100 countries, we provide reliable services, professional support, and on-time delivery, ensuring the power and reliability you expect for your car.

No matter if you’re looking to maintain, upgrade, or learn more about modern engines yourself, Woda is here to provide the highest-quality engine parts and expert support to extract the very maximum your cars have to offer.