The Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine is one of the most widely used small diesel engines produced in Europe over the past two decades. Known for its compact size, efficiency, and broad application across multiple vehicle brands, it has become a long-standing presence in the global automotive aftermarket.
Because of its large installed base and long production history, the 1.3 Multijet remains relevant today—not only for vehicle owners, but also for workshops, rebuilders, and parts distributors who continue to service and replace these engines worldwide.
This article provides a technical and practical overview of the Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine, covering its design, specifications, variants, reliability characteristics, and common service considerations.
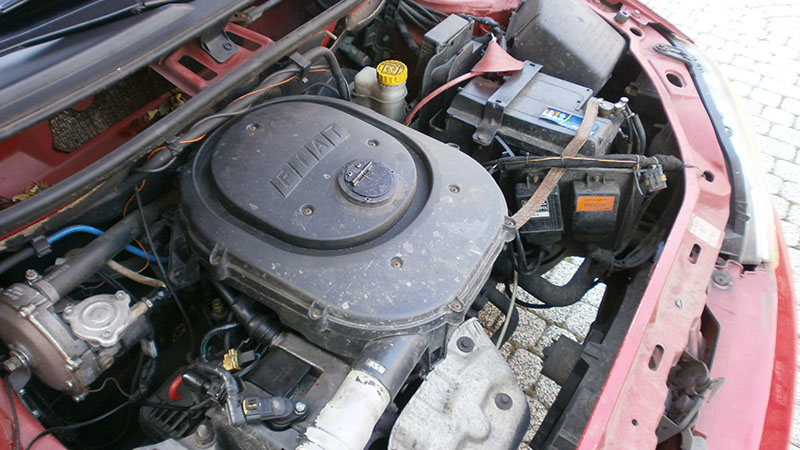

What Is the Fiat 1.3 Multijet Engine?
The Fiat 1.3 Multijet is a four-cylinder, turbocharged diesel engine developed by Fiat Powertrain Technologies. It belongs to Fiat’s JTD (Jet Turbo Diesel) family and uses common-rail direct injection with MultiJet technology, which enables multiple fuel injections per combustion cycle to improve efficiency, reduce combustion noise, and lower emissions.
The term “Fiat 1.3 Multijet” generally refers to this 1.248-liter diesel engine family and should not be confused with unrelated 1.3-liter petrol engines used in some Fiat models.
The engine was primarily developed for:
- Compact passenger cars
- Small sedans and hatchbacks
- Light commercial vehicles
Its balance of fuel economy, low-speed torque, and compact packaging has made it especially popular in Europe, Turkey, India, and other emerging markets.

Production Background and Market Presence
Since its introduction in the early 2000s, the 1.3 Multijet has been produced in very large volumes and installed across a wide range of vehicles. Over time, the engine family has evolved through multiple emissions standards and power outputs, including Euro 4, Euro 5, and Euro 6 versions.
Its long production run and cross-market adoption are key reasons why the engine continues to generate strong aftermarket demand today.
Fiat 1.3 Multijet Engine Specifications
The Fiat 1.3 Multijet is a 1.248-liter inline four-cylinder turbo diesel engine featuring a chain-driven DOHC valvetrain and common-rail MultiJet fuel injection. While it has been produced in multiple variants for different markets and emissions standards, its core mechanical architecture remains largely consistent across the engine family—one of the key reasons for its long production life and wide aftermarket support.
Core Technical Specifications
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Engine type | Inline 4-cylinder turbo diesel |
| Displacement | 1248 cc |
| Bore × stroke | 69.6 mm × 82.0 mm |
| Cylinder block | Cast iron |
| Cylinder head | Aluminum alloy |
| Valve configuration | DOHC, 16 valves |
| Fuel system | Common-rail direct injection (MultiJet / MultiJet II) |
| Aspiration | Turbocharged |
| Timing system | Chain-driven |
| Cooling system | Water-cooled |
| Emission standards | Euro 4 / Euro 5 / Euro 6 |
The combination of a cast-iron cylinder block and aluminum alloy cylinder head provides a balance between durability and weight, while the chain-driven timing system is designed for long service life when proper oil quality and maintenance intervals are observed.
Power and Torque Range
Depending on tuning, turbocharger configuration, and emissions level, the 1.3 Multijet is available in several output ranges:
| Version range | Output |
|---|---|
| Lower output | ~70–75 hp / ~180 Nm |
| Mid output | ~85–90 hp / ~190 Nm |
| Higher output (MultiJet II) | ~95 hp / up to ~200 Nm |
Torque is delivered at relatively low engine speeds, supporting efficient everyday driving and light commercial applications. Higher-output versions typically rely on refined injection strategies and updated turbo systems, rather than major mechanical changes to the engine block or rotating assembly.
MultiJet vs MultiJet II
Later MultiJet II versions introduced more precise fuel injection control and improved combustion efficiency, allowing the engine to meet stricter emissions standards while reducing noise and fuel consumption. Mechanically, the basic engine layout remains familiar, but electronic control systems and emissions-related components differ between generations.

Engine Variants and Key Differences
One of the defining characteristics of the Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine is the wide range of variants produced throughout its lifecycle. These differences are particularly important when it comes to servicing, rebuilding, or engine replacement, as not all versions are directly interchangeable.
Power and Calibration Variants
Common output levels include:
- 70 / 75 hp
- 85 / 90 hp
- 95 hp
While the base engine architecture remains largely the same, variations arise from differences in:
- ECU calibration
- Turbocharger specification
- Emissions-related components

Emissions Standards
Over time, the 1.3 Multijet evolved to meet stricter regulations:
- Euro 4
- Euro 5
- Euro 6
Each emissions stage introduced changes that can affect:
- EGR system design
- DPF integration
- Sensor layout
- ECU compatibility
Turbocharger Configuration
Lower-output versions typically use simpler turbocharger setups, while higher-output variants often feature variable-geometry turbochargers (VGT) to improve low-speed torque and overall efficiency.

Fiat 1.3 Multijet Engine Applications
The Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine has been widely used in a range of compact passenger cars and light commercial vehicles, particularly across European and emerging markets. Its compact dimensions, fuel efficiency, and strong low-speed torque made it well suited for both urban passenger use and small utility applications.
Common applications include:
- Fiat Punto / Grande Punto
- Fiat Panda
- Fiat 500 / 500L
- Fiat Linea
- Fiat Doblo
- Fiat Fiorino
- Fiat Egea (Tipo)
Depending on the model year and market, the engine has been offered in multiple power outputs and emissions configurations. As a result, specifications and hardware may vary even within the same vehicle line.

Cross-Brand Usage and Naming Differences
The Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine is closely related to, and in some cases directly shared with, diesel engines sold under different names by other manufacturers. Depending on the market and brand, it may be referred to as:
- DDiS
- CDTI
- Quadrajet
Although these engines share a common design origin, they are not always directly interchangeable without modification. Differences may exist in areas such as:
- ECU software and calibration
- Emissions control systems
- Ancillary components
- Engine mounting and accessories
For service or replacement purposes, it is essential to confirm the exact engine variant and specification, rather than relying solely on the engine family name.

Reliability Characteristics
Overall, the Fiat 1.3 Multijet has developed a reputation as a durable and efficient small-displacement diesel engine, especially when operated and maintained according to recommended service intervals. Its long production run and widespread use have also contributed to a well-established service and parts ecosystem.
Key strengths commonly associated with the engine include:
- Good fuel efficiency, particularly in mixed urban and highway driving
- Strong low-speed torque for its displacement, supporting everyday drivability and light commercial use
- Long service life when proper oil quality and maintenance schedules are followed
- Wide availability of parts, including both OEM and aftermarket components
As with most modern common-rail diesel engines, long-term reliability is heavily influenced by maintenance quality, fuel cleanliness, and operating conditions. Engines subjected to regular short trips, inconsistent service, or poor fuel quality are more likely to experience emissions-related or fuel-system issues, whereas units operated at stable temperatures with consistent servicing generally deliver more predictable and durable performance.
Common Issues and Service Patterns
Across different markets and applications, several recurring service areas are commonly observed. These issues do not affect every engine but tend to appear under specific driving patterns and maintenance conditions.
EGR and Intake Contamination
Engines used primarily for short-distance or urban driving may experience:
- EGR valve clogging
- Intake carbon buildup
These issues are typical of modern diesel engines operating at low exhaust temperatures.
Fuel System Sensitivity
The common-rail injection system requires:
- Clean fuel
- Proper filtration
Injector wear or fuel-related issues are more likely to occur in regions with inconsistent fuel quality.
Turbocharger Wear
Turbocharger lifespan is influenced by:
- Oil quality
- Oil change intervals
- Operating temperature
Versions equipped with variable-geometry turbochargers (VGT) can be more sensitive to soot buildup if maintenance is neglected.
DPF-Related Issues (Later Versions)
Engines fitted with diesel particulate filters may experience regeneration-related problems if the vehicle is frequently driven at low speeds or over short distances.
Timing Chain Considerations
The 1.3 Multijet uses a chain-driven timing system. While generally durable, timing chain noise or wear can occur in high-mileage engines or those with poor oil maintenance history.

Service Life and Rebuild Potential
In real-world operation, the Fiat 1.3 Multijet is capable of reaching high mileage before major mechanical intervention is required, provided that regular servicing and correct oil specifications are maintained. Its design prioritizes durability and efficiency, which has contributed to its long service presence across multiple markets.
From a technical perspective, the engine:
- Features a robust cast-iron cylinder block and a well-designed aluminum cylinder head
- Is well suited to professional rebuilding, with clear machining tolerances and established overhaul procedures
- Benefits from wide availability of internal components, including bearings, pistons, rings, and valve train parts
In practice, overall engine condition, service history, and operating environment have a greater impact on longevity than the basic engine design itself. Engines maintained with consistent oil changes and operated at proper working temperatures typically offer predictable service life, while those subjected to neglected maintenance or unfavorable operating conditions are more likely to require earlier rebuild or replacement.

Replacement and Rebuild Considerations
When evaluating replacement or rebuild options for the Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine, accurate identification and compatibility assessment are essential. Although many versions share a similar base architecture, differences between variants can significantly affect installation and long-term performance.
Key factors to confirm include:
- Correct engine variant and power rating, as differences in calibration and hardware exist across versions
- Matching emissions standard (Euro 4, Euro 5, or Euro 6), which determines EGR configuration, DPF presence, and sensor layout
- ECU and sensor compatibility, particularly when replacing complete engines rather than rebuilding the original unit
- Turbocharger specification and fuel system condition, as these components vary by output level and emissions stage
Common replacement strategies include:
- Used take-out engines, typically chosen for cost-sensitive or time-critical repairs
- Professionally rebuilt engines, offering more consistent quality and predictable service life when rebuilt to defined standards
- Long block or short block solutions, allowing reuse of existing ancillaries and electronics when compatibility permits
Regardless of the chosen approach, a clear definition of what is included—such as whether injectors, turbocharger, fuel pump, wiring, or ECU are supplied—is critical. Clarifying these details in advance helps avoid installation issues, reduces downtime, and ensures the replacement engine meets both mechanical and electronic requirements.

FAQ
Is the Fiat 1.3 Multijet chain or belt driven?
The engine uses a chain-driven timing system.
Are all 1.3 Multijet engines interchangeable?
No. While they share a common design, differences in power output, emissions equipment, ECU calibration, and accessories must be considered.
Is the 1.3 Multijet suitable for long-distance driving?
Yes. Engines used regularly at operating temperature tend to experience fewer EGR and DPF-related issues than those used only for short trips.
What are the most common problems with the Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine?
Typical issues include EGR clogging, injector wear, turbocharger faults, and DPF regeneration problems on later emissions versions. Maintenance quality and driving conditions play a major role.
How long does a Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine typically last?
With proper servicing, the 1.3 Multijet is capable of high mileage before major mechanical work. Longevity depends mainly on maintenance, operating conditions, and fuel quality.

Conclusion
The Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine remains a widely used and well-supported diesel platform. Its long production history, multiple variants, and broad vehicle coverage have ensured continued relevance in service, repair, and replacement markets worldwide.
For those working with this engine—whether in diagnostics, rebuilding, or sourcing—understanding variant differences, emissions requirements, and real-world service patterns is essential. When correctly identified and properly maintained, the 1.3 Multijet continues to offer dependable performance and predictable service life.
About Us
Woda Auto is an automotive engine and engine components manufacturer with over 25 years of industry experience, supplying complete engines, cylinder heads, and core engine components to global B2B markets. We focus on stable quality, accurate specification matching, and long-term supply reliability.
If you are sourcing Fiat 1.3 Multijet engines or related engine components for your business, you may contact our team to discuss product availability and cooperation opportunities.