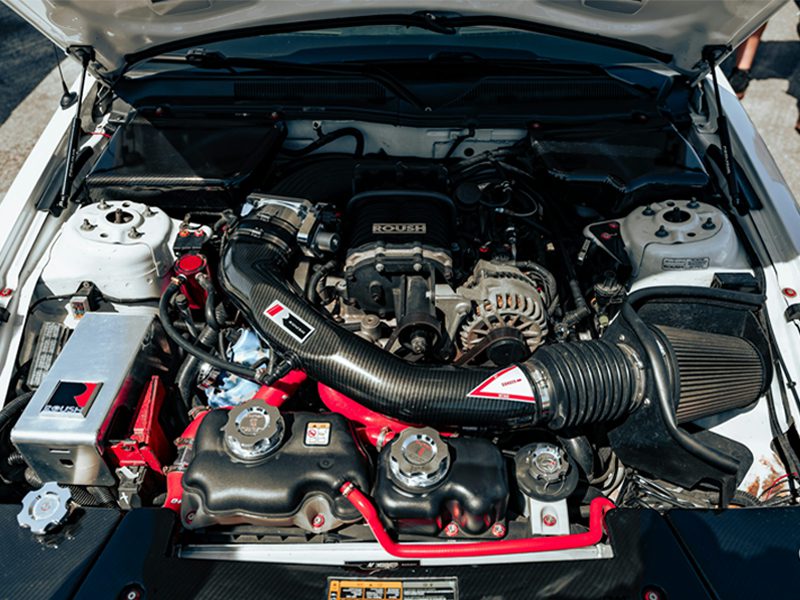
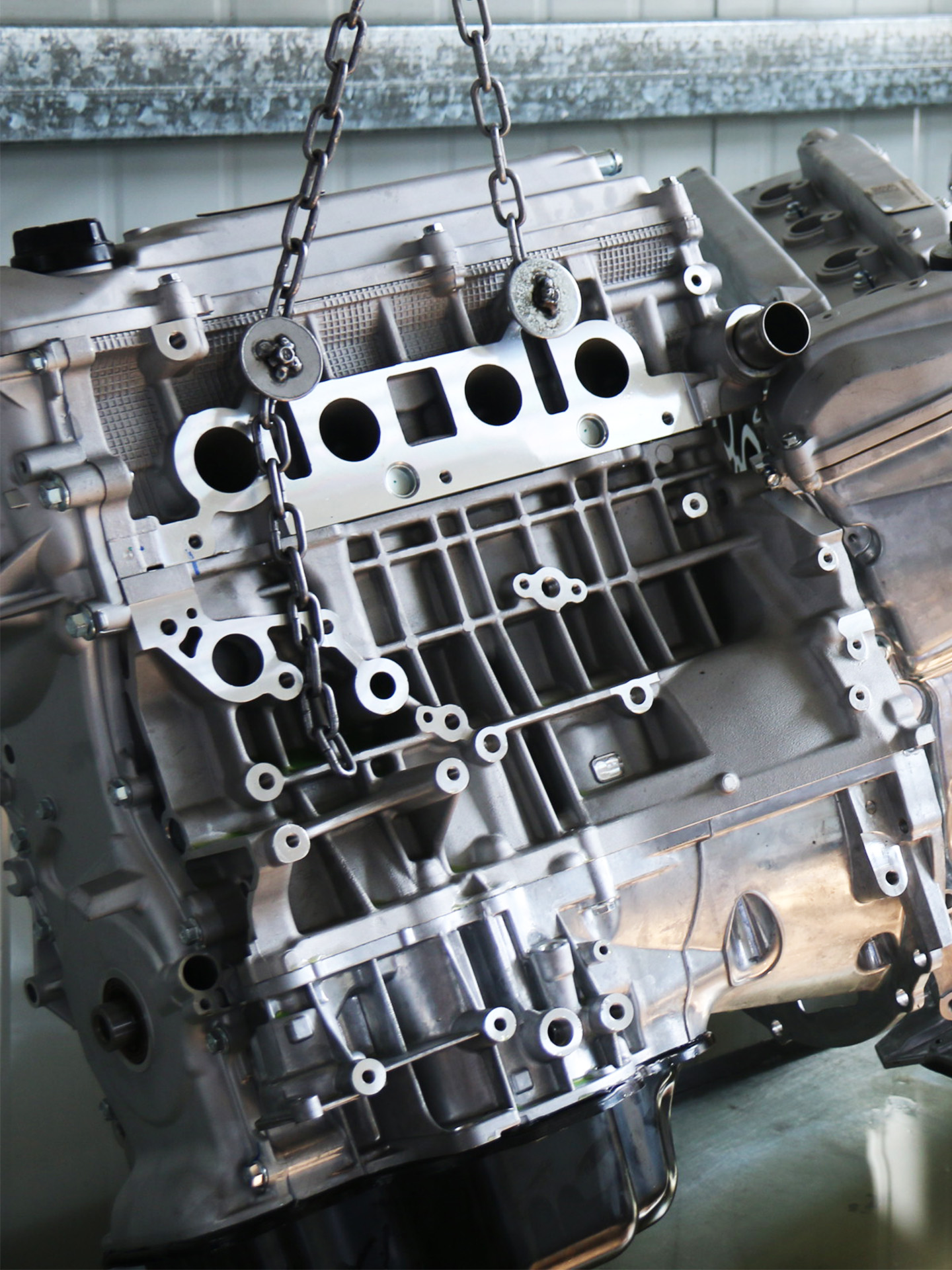
Think of the intake manifold as the lungs of your engine and your vehicle—without it, your car wouldn’t be able to breathe. The intake manifold is tasked with delivering a precise mix of air (and sometimes fuel) to each cylinder, dictating how efficiently and powerfully your engine runs at all times.
A fully utilized intake manifold can unlock horsepower, improve throttle response, and even boost fuel economy, while a failing one can choke performance and lead to major repairs.
No matter if you’re troubleshooting issues, running a repair shop, or chasing extra horsepower, this guide will help you master the intake manifold, so stick around and learn how to unleash your engine’s full potential!

What Is an Intake Manifold?
So, what does an intake manifold do? As the introduction mentions, the air intake manifold takes in air through the air filter and distributes it to the engine’s cylinders through the intake ports.
In older vehicles or those without direct injection, the air intake manifold also regulates fuel delivery via the inlet valve spraying fuel droplets into the incoming air, a system known as port fuel injection (PFI).
Intake manifold housings tend to be made out of either aluminum or cast iron. Aluminim is lighter, dissipates heat very well, and is corrosion resistant while cast iron air intakes are more durable, yet way to heavy for modern-day cars.
Some vehicle engines also use plastic intake manifolds, but in general, these are not the recommended. Be that as it may, intake manifold maintenance is often even more crucial that the material and how it’s assembled.

Key Intake Manifold Design Factors to Know About
Numerous factors affect how well an intake manifold operates, but its design and placement are key to maximizing an engine’s volumetric efficiency and performance.
Most modern air intake manifolds feature runners—individual tubes extending to each intake port on the cylinder’s head—all branching from a central chamber, or plenum, located beneath the throttle body.
Such a design is essential for proper air distribution during the first combustion stroke, maximizing both vehicle output and efficiency in every internal combustion engine and combustion chamber cycle.
Another smart feature of most modern intake valve manifolds is their ability to circulate coolant through the manifold to the cylinder heads, helping to keep engine coolant into the engine cylinders and regulate optimal engine temperatures.
Lastly, it’s important to mention the intake manifold gasket, a small yet crucial component that seals the connection between the cylinder heads and the manifold. The gasket prevents vacuum leaks, coolant leaks, and unmetered air entering the inlet manifold, all of which can negatively impact the engine and the valve timing.

Plastic vs Aluminum vs Cast Iron Intake Manifolds: Pros and Cons
If you’ve ever wondered what will an aluminum intake manifold do or what are the benefits of aluminum intake manifold over iron or plastic, here is what you need to consider.
| Material | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Plastic Manifold | Extremely lightweight, cost-effective, reduces heat soak | Can crack/warp under extreme heat, less durable |
| Aluminum Manifold | Durable, heat-resistant, good for race combustion | Relatively heavy, more expensive, absorbs heat |
| Cast Iron Manifold | Extremely strong, highly wear-resistant | Extremely heavy, retains high temperature, less common today |

Single vs Dual-plane Intake Manifolds
There are a few important differences one needs to understand between single plane and dual plane intake manifolds, but in short, single plane means horsepower while dual plane means torque.
Single-Plane Intake Manifold System
- Designed for high-RPM performance, commonly used in racing and high-horsepower builds.
- Provides faster airflow, improving top-end grunt but sacrificing low-end torque.
- Perfect for drag racing, track cars, and high-revving engines.
Dual-Plane Intake Manifold System
- Designed for low to mid-RPM efficiency, making it suitable for street-driven vehicles and daily use.
- Splits the intake plenum into two separate passages, improving throttle response and low-end torque.
- Best suited for vehicle street performance, towing, and moderate performance cars and other vehicles.

Short-Runner vs Long-Runner Intake Manifolds Systems
Short-runner manifold solutions utilize short, wide passages that allow air to move quickly, also making them ideal for high-RPM performance vehicles and maximizing horsepower.
In contrast, long-runner manifolds use longer, narrower passages to slow airflow, improving low-end torque and vehicle throttle response.
The choice for you primarily depends on what you are after—short runners for top-end speed, long runners for low-end and efficiency.

How Does an Intake Manifold Boost Performance?
The intake manifold is primarily tasked with distributing air, which means that it aims to always send uniform amounts of air to each side of the inlet cylinder’s head.
Direct injection engines vehicles rely on the intake manifold only for the delivery of air while port injection engines use the inlet manifold to also deliver droplets of fuel. The key to achieve the maximum out of a manifold in both cases is how efficient they are.
This is where streamlined fluid-dynamic designs come into play, allowing for maximum volumetric efficiency, which ensures better airflow, improved combustion chamber performance, and optimal engine operation.
This optimized airflow also enables scavenging and Helmholtz resonance, two principles that further help improve engine efficiency, mechanical output delivery, and overall performance.

What is an Intake Manifold Gasket?
The intake manifold gasket is tasked with a crucial role in sealing the connection between the intake manifold and cylinder heads. If it fails to do that, it can lead to bad subpar efficiency, misfiring, and power loss.
5 Signs An Intake Manifold Gasket is Failing
- Vacuum Leaks – If the gasket goes haywire, unmetered air will likely enter the inlet manifold and your car migh experience bad idling, misfires, and poor performance.
- Coolant Leaks -If the gasket fails directly near a coolant passage/line, it can lead to coolant loss, overheating, and potential temperature-related engine damage.
- Bad Fuel Efficiency – If your car is burning through more fuel than usual, a faulty intake manifold gasket could be disrupting the air-fuel ratio, leading to reduced efficiency.
- Hissing or Whistling Noises – A leaky gasket can produce audible hissing or whistling sounds, indicating escaping air and an improper seal, especially when revving.
- Check Engine Light (CEL) – The ECU tends to detect irregular air intake valve operatio and fuel delivery cycles and is likely to trigger a check engine light.

How to Repair the Intake Manifold Gasket?
If you do face some of the symptoms of a failing/failed intake manifold gasket, the best idea would be to resolve them immediately since a failing air intake manifold gasket can easily lead to costly engine damage, and the best thing to do would be to simply replace it.
To replace a failing intake manifold gasket, first diagnose the issue by checking if some of the previously mentioned symptoms are present while also using a connected OBD-II reader to scan the car for relevant codes.
The intake manifold must be carefully removed, ensuring that sealing surfaces are cleaned before installing the new gasket as that is going to minimize future wear and tear.
A good idea would also be to always make sure to properly torque the inlet manifold bolts to prevent leaks and ensure a tight, secure seal. Checking relevant repair manuals to see how torqued these ought to be, is very much recommended.
After installation, check for vacuum valve leaks and coolant circulation to confirm the repair was successful while also clearing all of the codes.

How to Maintain the Intake Manifold Gasket?
The very best way to prevent any of the aforementioned intake manifold gasket issues is to regulary maintain it. This helps prevent vacuum leaks, coolant leaks, and all kinds of engine pressure inefficiencies.
It’s recommended to inspect the inlet manifold and gasket area periodically for signs of a bad intake manifold such as cracks, warping, or leaks, as early detection can prevent major repairs.
Keeping the cooling system in optimal condition is also very important, as too much warmth can degrade the gasket over time, especially if its heat-repellant properties are worn out.
Using high-quality coolant and ensuring the system is properly filled at all times can extend the gasket’s lifespan.
Lastly, when replacing the gasket, opting for durable, heat-resistant materials can further improve engine reliability and efficiency, so be sure to keep this in mind.

Intake Manifold Upgrades: Key Modifications That Work
In the world of high-performance tuning, upgrading or modifying the intake manifold can significantly improve engine grunt, as such modifications enhance inlet air flows, potentially boosting power or optimizing fuel efficiency for your internal combustion engine cylinder heads.
However, the impact depends on engine setup, intake valve timing, the plenum, pressure, tuning, and supporting modifications.
Sometimes, the balance leans toward more power or better fuel efficiency, depending on the air inlet manifold design and how it interacts with the engine’s air-fuel mixture.
Variable-lenght intake manifolds (VLIMs) are one of the most popular mods, and there a few things you ought to consider before spending your money.

As mentioned, short intake runner manifolds favor high-RPM horsepower, while long-runner manifolds improve low-end torque and efficiency.
To maximize the benefits, these should always be paired with proper map tuning, complementary engine hardware modifications and separate component mods such as intake manifold intake runners, cylinder heads mods, and intake controls which further optimize air distribution.
However, when replacing or modifying the intake manifold, it’s crucial to consider the inlet, timing and air-fuel aspect ratios to optimize engine workings while avoiding potential drawbacks.

FAQs
1. What does a manifold intake do?
The intake manifold evenly distributes the air (or air-fuel mixture) to each cylinder in the engine. This ensures:
- Optimal combustion
- Smooth engine performance
- Improved fuel efficiency
In some designs, the manifold also houses sensors or supports variable intake tuning for better power and torque delivery.
2. What happens when the intake manifold is bad?
A failing intake manifold can cause several issues, including:
- Engine misfires or rough idling
- Coolant leaks (if the manifold is integrated with coolant passages)
- Reduced power and poor fuel economy
- Illuminated Check Engine Light
Cracks or gasket failures can also lead to vacuum leaks, which disrupt air-fuel ratios.
3. Can I drive my car with a bad intake manifold?
You can drive short-term, but it’s not advisable. A bad intake manifold can lead to:
- Engine overheating (if coolant is leaking)
- Unstable idling or loss of power
- Increased emissions and long-term engine damage
It’s best to diagnose and repair the issue promptly to avoid higher repair costs.
4. Where is the intake manifold located?
The intake manifold is mounted on the top or side of the engine, directly connected to the cylinder head(s). It sits between the throttle body and the engine block, routing air or the air-fuel mixture from the intake system into the combustion chambers.
5. How much does it cost to replace an intake manifold?
The replacement cost depends on the vehicle’s make and model, but typically ranges from:
- $300 to $700 for parts
- $200 to $500 for labor
Total replacement may cost between $500 and $1,200. Complex intake systems or labor-intensive jobs may push the cost higher.
Closing Thoughts on Intake Manifolds: Key Takeaways for Professionals
Knowing the intricacies of the intake manifold can help you break into an engine’s full pressure potential. After all, the intake manifold plays a vital role in how air reaches the engine.
To fully optimize its benefits, one must prioritize proper diagnostics, routine maintenance, and sourcing the right parts. For professionals, partnering with the right parts suppliers can be the difference between seamless operations and costly downtime.
If you are looking for high-quality aftermarket parts and a dedicated supplier, Nanjing Woda Auto Technology Co., Ltd. has been a trusted name in the automotive parts industry for 25 years!

Based in Nanjing, China, we specialize in engine systems, ignition systems, electrical systems, and exhaust components, among others, offering comprehensive B2B procurement solutions for businesses worldwide!
With over 100,000 products exported to 100+ countries, we offer OEM-grade quality, competitive pricing, and dedicated after-sales support to distributors, wholesalers, and industry professionals! Be sure to get in touch!