Your car’s shaking. The check engine light is flashing. You scan the code: P0300-00 engine misfire detected! Random/multiple cylinder misfire occurs. What now?
Don’t guess — diagnose. The P0300 code troubles thousands upon thousands of drivers every year, and one thing is always the same: it never shows up at a convenient time.
This guide walks you through exactly what’s going wrong, how to fix it, and what to do to save your engine (and your wallet). So, if you want to know more about the P0300 engine code, stick around and find out!

What is the P0300 Code?
The P0300 code is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that signals random or multiple misfires — meaning the engine’s cylinders aren’t firing as well as they should.
Whenever this issue occurs, the car’s ECU detects it and thus prompts the P0300 code. In general, the code can be caused by all kinds of issues, including faulty ignition system components, clogged injectors, and low fuel pressure.
Top 5 Common Symptoms of the P0300 Code
The most common symptoms of the P0300 code include:
- Hard starting: The engine struggles to turn over or takes longer than usual to kick into life. This is usually more noticeable in winter weather or after the car sits for a bit.
- Hesitation or stumbling: You might also feel the car hesitating, lurching, or stumbling when under acceleration. If one or more cylinders aren’t firing consistently, you will likely experience this.
- Rough idle or reduced performance: The code P0300 also makes the car shake at idle, feel unsteady, or lack overall power while accelerating.
- Engine Check Light: The P0300-00 engine misfire detected code will also turn on the dreaded CEL. This is the car’s first warning that something isn’t right.
- Flashing check engine light: If the misfire occurs and is severe or ongoing, the CEL light might even begin flashing. This indicates a risk of damaging the catalytic converter and should be addressed asap.

Top 6 Common Causes of the P0300 Code
Here are the most common culprits of the P0300 engine code:
- Faulty Spark Plugs or Damaged Spark Plug Wires: Old or damaged plugs often refuse to ignite the air-fuel mixture or make it unbalanced. If that indeed does happen, it will likely cause misfires.
- Faulty Ignition Coil Packs or Faulty Crankshaft Sensor: It’s the same story with a failing ignition coil, which can lead to intermittent spark. Similarly, a malfunctioning crankshaft sensor can also mess up ignition timing and confuse the ECU, which in turn might not be able to control the timing.
- Clogged Fuel Injectors or Faulty Fuel Pump: Dirty or partially blocked injectors are also known to disrupt the proper amount of fuel entering the chamber. A weak fuel pump reduces fuel pressure and thus contributes to misfiring.
- Low Fuel Pressure or Vacuum Leaks: We also need to talk about low pressure within the fuel lines, which causes cylinders to run overly lean. Vacuum leaks can also introduce unmetered air into the engine, which disrupts the air-fuel ratio and leads to misfiring.
- Defective Camshaft Sensor: The camshaft position sensor helps the ECU sync fuel injection and spark timing. If it’s a faulty camshaft position sensor, the engine experiences timing issues and leads to misfires.
- Catalytic Converter and Exhaust System Problems: A clogged catalytic converter can increase exhaust leak backpressure, disrupting combustion and causing engine misfires. In any case, damage or blockage elsewhere in the exhaust system can trigger a P0300 fault code.

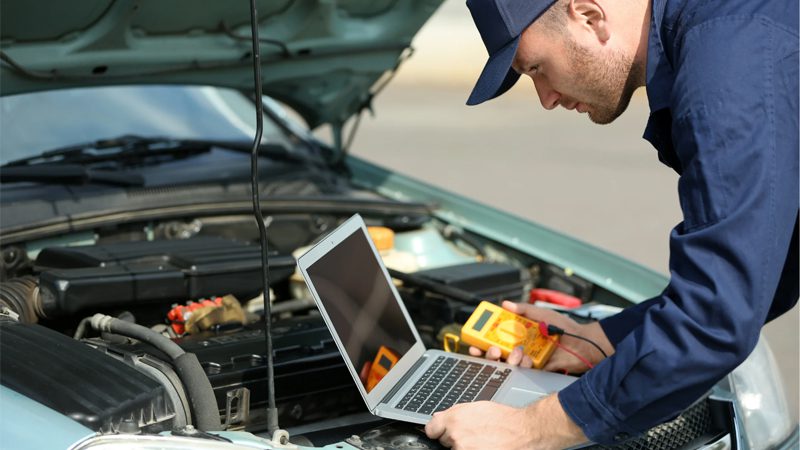
How to Diagnose the P0300 Fault Code Like a Pro (Step-by-Step)
Successfully diagnosing a P0300 engine code can take a bit of good old digging, but following a structured and logical approach makes it so much easier. Here’s how to narrow down the root cause and properly diagnose the P0300 code:
Step 1: Scan for Additional Fault Codes
The first step would always be to use an OBD2 scanner to make sure the P0300 is truly to blame. In most instances, your OBD2 will also check for related codes such as the P0301, P0302, etc.
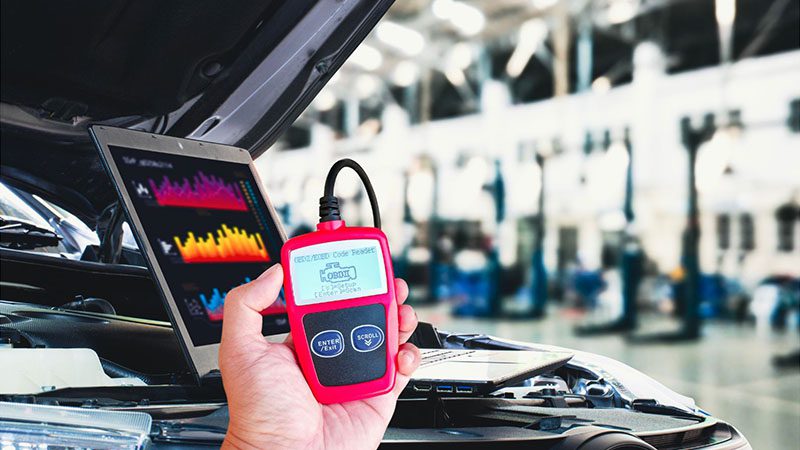

The idea behind these is to point you to a specific cylinder that might be misfiring, which will help you pinpoint the issue in no time.
Step 2: Inspect Ignition Components
You can also remove and check the spark plugs for signs of wear, fouling, or damage, as those are often related to the P0300 code.
Also, it would be a good idea to test the ignition coils and coil packs as well as spark plug wires — a weak or intermittent sparking sequence is a well-known cause of misfires.
Step 3: Test Fuel Delivery
We already mentioned that the P0300 code can be related to fuel delivery system trouble, including issues with the fuel filter. In order to diagnose those, check the fuel filter and injectors for proper spray pattern and operation.

If in any way possible, perform a fuel pressure test to see if the fuel pump is delivering adequate pressure at all times.
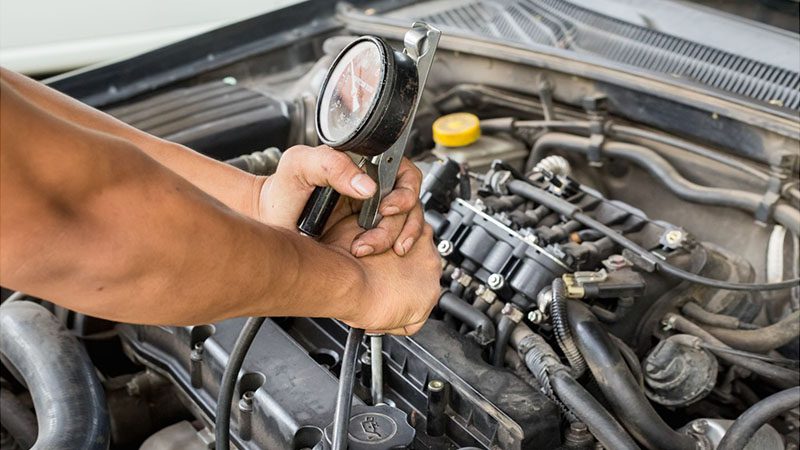
Step 4: Perform a Compression Test
Low operation compression within one or more cylinders can indicate internal engine issues like worn–out piston rings, a bad valve, or a blown head gasket.
Use a compression gauge to test each cylinder and make sure all readings are up to scratch. If not, it is most likely due to the P0300 fault code.
Step 5: Investigate Further if Needed
If you’ve gone through all of these steps and no clear cause is found, consider checking for vacuum leaks, timing issues, or ECM-related problems.
Sometimes the misfire is a symptom of a deeper issue, one that can only be diagnosed if you take your car to an experienced mechanic who has all of the right tools and knowledge.

How to Fix the P0300 Code: What to Repair and Replace?
In most cases, replacing worn spark plugs or a faulty ignition coil is enough to resolve the P0300 trouble code. It is usually what causes the P0300 and, thankfully, is a fairly easy thing to resolve. Simply buy ones and replace the old ones.
However, if the misfires are linked to fuel delivery problems, cleaning or replacing a clogged fuel injector may be the way to go. Similarly, if testing reveals low fuel pressure, the fuel pump or pressure regulator might need some attention.
Vacuum leaks are often overlooked when it comes to the P0300, but are known to be problematic. Cracked hoses, bad connections, or failing intake gaskets can let in rogue air, disrupting the air-fuel mixture. To make this go away, find the vacuum leak and be sure to fix it.

In some cases, incorrect engine timing might be to blame, possibly due to a faulty PCM or a defective PCM. This is more likely to happen if you’ve recently had work done on the timing chain or belt. Retiming the engine can eliminate these problems, so keep that in mind.
In the case of a malfunctioning/clogged catalytic converter, replacing the converter or repairing the affected section of the exhaust may be necessary to fully restore proper flow and eliminate backpressure-related misfires.
More serious problems, such as a blown head gasket or internal engine damage, may require a top-end overhaul. Even though this is more labor-intensive, it’s sometimes the only way to restore proper engine operation.

Understanding P0300 and Associated Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
There are also many other bb codes associated with the dreaded code P0300, and these are the ones to look out for the most.
| Code | Meaning | What It Typically Indicates |
|---|---|---|
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | A misfire isolated to cylinder 1 — helps narrow down the root cause. |
| P0302 | Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected | Misfire in cylinder 2 — continue testing ignition and fuel components. |
| P0303 | Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected | Misfire in cylinder 3 — check spark plug, coil, and injector on that cylinder. |
| P0304 | Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected | Misfire in cylinder 4 — isolate the problem to ignition or fuel delivery there. |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Too much air or not enough fuel — caused by vacuum leaks or bad fuel pressure. |
| P0174 | System Too Lean (Bank 2) | Similar to P0171, but on the opposite engine bank — check for air. |
| P0350 | Ignition Coil Primary/Secondary Circuit Malfunction | Electrical issue in ignition coil wiring or the control circuit. |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Often linked to a failing catalytic converter, it may be caused by misfires. |
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Performance Issue | MAF sensor not reading as it should — disrupts air and fuel ratio and causes misfires. |
| P0130 P0167 | Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (various banks/sensors) | Faulty O2 sensors can trick the ECU, leading to incorrect fuel timing. |

How Much Does It Cost to Fix a P0300 Code?
Since there are so many potential causes of the P0300 engine trouble code, including other OBD II codes, it’s fairly difficult to say how much it might cost to remedy it completely. However, for a broader understanding of what it might cost to fix the P0300 fault code, be sure to check the chart below.
| Repair/Part | Estimated Cost (Parts & Labor) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Spark Plug Replacement | $100 – $300 | Cost varies by vehicle and spark plug type (copper, platinum, iridium). |
| Ignition Coil Replacement | $150 – $500 | Some vehicles have individual coils per cylinder, increasing total cost. |
| Fuel Injector Cleaning/Replacement | $150 – $600 | Cleaning is cheaper; replacement costs more depending on access. |
| Fuel Pump Replacement | $400 – $1,000 | Labor-intensive on some models; includes drop-in pump or assembly. |
| Vacuum Leak Repair | $150 – $500 | Includes hose replacement or intake gasket resealing. |
| Exhaust Leak Repair | $200 – $1,000 | Cost depends on the leak location and severity. |
| Catalytic Converter Replacement | $800 – $2,500+ | High cost due to precious metals; OEM parts cost more than aftermarket. |
| Sensor Replacement (MAF/O2) | $100 – $400 | MAF and oxygen sensors are common misfire culprits. |
| Compression Test & Diagnosis | $100 – $250 | Often used to confirm internal engine issues. |
| Engine Top-End Overhaul | $1,000 – $3,000+ | Needed only in severe cases (e.g., blown head gasket, valve issues). |
Preventing the P0300 Code: Maintenance Tips That Work!
It’s always better to prevent a problem rather than fix it, which is why we’ve compiled a few useful tips and tricks on how to never encounter the P0300 code.
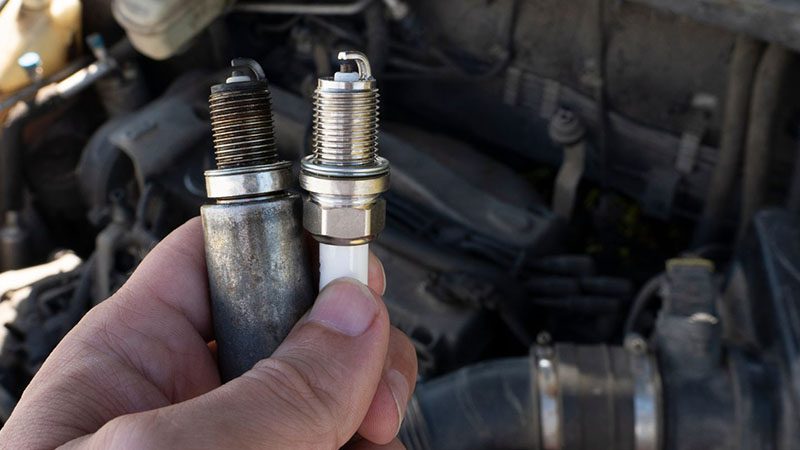
Replace Spark Plugs and Wires on Time
Worn spark plugs and aging wires are among the most common causes of misfires. Stick to your vehicle’s recommended replacement intervals and always make sure to replace your spark plugs in due time.

The best thing to do would be to always have a repair manual nearby and follow it as diligently as you can.
Keep the Fuel System Clean
Another good idea would be to use fuel system cleaners, as these can help prevent clogged injectors, and this reduces the chances of ever experiencing the P0300 code.
High-quality fuel, along with a properly functioning airflow sensor, is also going to aid in long-term proper fuel delivery, so be sure to treat your car to premium fuel from time to time.
Inspect Ignition Components Regularly
Ignition coils, plug boots, and connectors should always be checked for wear or corrosion during routine service. This means that, whenever accessible, make sure to tell your mechanic to inspect these.
Some people choose to replace ignition coils periodically, even before they fail, since low-quality or aging coils can cause a range of issues, not just the P0300 code.
Address Check Engine Lights Promptly
Don’t ignore early warning signs — small issues can snowball into costly misfires if left unresolved. So, if you do come across a CEL, make sure to always diagnose it and take care of the problem.
If you want to know everything there is to know about how to approach fixing a CEL, be sure to click here.

Frequently Asked Questions
What Does the P0300 Code Mean?
The P0300 code indicates random or multiple cylinder misfires in the engine, meaning one or more cylinders aren’t firing properly and are in need of dire attention.
Can a Bad O2 Sensor Cause a P0300 Code?
Yes. A faulty oxygen sensor can indeed send incorrect data to the ECU, which is going to lead to an unbalanced air-fuel mixture and misfires.
Will a Misfire Clear Itself?
Occasionally, a minor misfire may stop temporarily, but the underlying issue will usually return unless properly diagnosed and fixed. It all depends on what might be causing the misfire in the first place.
How Do I Fix P0300 Fast?
Start by scanning for additional codes, which can point you to a specific cylinder that might be misfiring, then check spark plugs, ignition coils, and fuel injectors — these are the most common causes of the P0300 code.
Can Dirty Fuel Injectors Cause a P0300 Code?
Yes, they can. Clogged or failing fuel injectors tend to lead to uneven fuel delivery, causing misfires across multiple cylinders, potentially making it even worse over time.
P0300 Code Summary & Where to Get the Right Parts!
The P0300 code signals random or multiple cylinder misfires within the engine — a fairly serious issue that can lead to engine damage if not addressed in due time.
At the most essential level, always begin with the basics: inspect the ignition system, check fuel delivery, and verify engine timing. These critical powertrain systems naturally wear down over time and will eventually require replacement, and this is where we come in.
Shop high-quality ignition coils, spark plugs, fuel injectors (and a lot more) at Nanjing Woda Auto Technology Co., Ltd.
With over 25 years of experience, Nanjing Woda is a trusted global supplier based in China, offering one-stop sourcing for engine, ignition, exhaust, suspension, and electrical systems. Our products are exported to 100+ countries, backed by competitive pricing, reliable shipping, and expert support.
For bulk orders or OEM/aftermarket engine components, contact us today — and get your engine running as it should!