The timing system is one of the unsung heroes under your car’s hood. It keeps the crankshaft and camshaft rotating in perfect sync, ensuring the engine’s valves and pistons work together at the proper time for smooth and efficient operation.
When this system is running as it should, your engine performs at its best—and avoids unnecessary wear and tear.
Depending on your vehicle, this job is handled by either a timing belt or a timing chain, each with its own pros and cons. Timing chains are built for longevity and are lubricated by engine oil, while timing belts tend to run more quietly and often come with simpler maintenance routines.
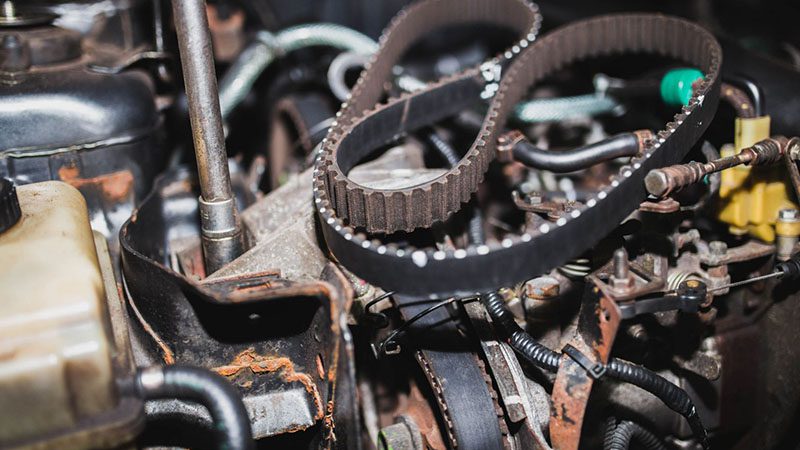

Not sure which one your car has? A quick check of your owner’s manual will tell you, along with the recommended replacement interval. Staying on top of this can save you from costly engine repairs down the road.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the key differences between timing belts and timing chains, break down their advantages and drawbacks, and help you determine which option makes the most sense for your engine—and your budget.
What Is a Timing Belt?
A timing belt is a toothed rubber belt that keeps your engine’s crankshaft and camshaft turning in sync. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the engine’s internal components work together at the right time.
Compared to timing chains, timing belts are generally cheaper to manufacture and replace, which is why many carmakers have favored them for years.
However, timing belts come with a downside—they can fail without much warning, potentially leading to serious engine damage and expensive repairs.
Since the water pump is often driven by the timing belt, it’s common practice to replace both at the same time to avoid extra labor costs later on. Similarly, idler pulleys, tensioners, and other related components might also need attention during a timing belt service.
Despite these risks, many manufacturers still choose timing belts because of their lower cost, lighter weight, and quieter operation, especially in vehicles designed for smooth and economical driving.

What Is a Timing Chain?
A timing chain does the same job as a timing belt—keeping the crankshaft and camshaft synchronized—but it’s made of durable metal links, much like a bicycle chain.
Thanks to its rugged design, a timing chain is built to last the lifetime of the engine in many cases, making it a popular choice in modern vehicles where long-term reliability is a priority.
Because timing chains run inside the engine, they are constantly lubricated by engine oil, which helps reduce wear and extend their lifespan. That said, they’re not entirely maintenance-free.
Lack of oil changes, dirty oil, or high mileage can cause the chain, tensioners, or guides to wear out, leading to noise, reduced power, performance issues, or even chain failure over time.
While timing chains tend to be noisier and more expensive to replace than timing belts, many drivers appreciate the peace of mind they offer by eliminating the need for scheduled replacement intervals.
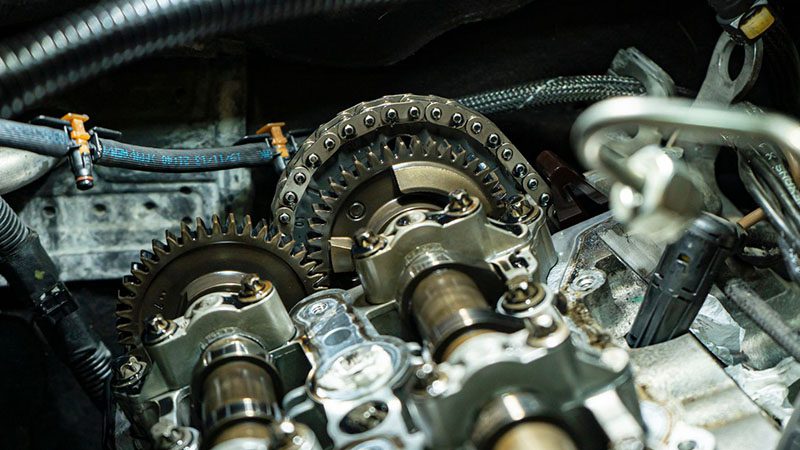
Timing Belt vs. Timing Chain: Key Differences
While both timing belts and timing chains perform the same essential role of synchronizing the engine’s crankshaft and camshaft, they don’t do it in the same way—differing significantly in material, maintenance needs, and lifespan.
Here’s a quick comparison of the key differences:
| Feature | Timing Belt | Timing Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Rubber with reinforced fibers | Metal links |
| Durability | 60,000–100,000 miles | Often lasts the life of the engine |
| Maintenance | Regular replacement needed | Low maintenance if oil is well-kept |
| Failure Risk | Can fail suddenly | Rare, but possible with poor upkeep |
| Noise Level | Quieter | Louder |
| Cost to Replace | Lower | Higher |
| Installation Location | Outside engine block | Inside engine, oil-lubricated |
| Additional Components | Often linked to water pump, pulleys | Uses tensioners and guides |

Note on Timing Gears
While timing belts and chains dominate most modern engines, some older or heavy-duty applications still use timing gears. These systems use metal gears for direct connection between the crankshaft and camshaft, offering exceptional durability and precision. However, they are heavier, noisier, and more expensive to manufacture, which is why they are rarely used in today’s passenger vehicles.
Maintenance & Replacement Considerations
When it comes to maintenance, timing belts and timing chains follow very different schedules.
Timing Belts
Timing belts require proactive replacement at intervals typically ranging from 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the vehicle and manufacturer’s recommendations.
Ignoring this maintenance can lead to sudden belt failure, potentially causing catastrophic engine damage. It’s also common to replace related components like the tensioner, idler pulleys, and water pump during a timing belt service, as they wear alongside the belt.

Timing Chains
On the other hand, timing chains are generally designed to last the life of the engine, assuming the engine is properly maintained.
Since timing chains operate inside the engine and rely on clean, well-lubricated oil, regular oil changes are critical to prevent premature wear of the chain, tensioners, and guides.
While timing chains don’t have a set replacement interval, they can stretch or wear over time, especially in high-mileage or poorly maintained engines, eventually requiring inspection or replacement.

Conclusion
Understanding the differences between timing belts and timing chains can help car owners stay on top of their vehicle’s maintenance needs and avoid costly surprises down the road.
While most vehicles come equipped with one or the other based on the engine design, knowing how these systems work—and their unique maintenance requirements—can help you make smarter decisions when it comes to service schedules or purchasing a used car.
At Nanjing Woda Auto Technology Co., Ltd, we specialize in providing high-quality engine and transmission parts for a wide range of vehicles. From timing components to complete engine assemblies, our products are engineered for durability, precision, and performance.
Whether you’re a workshop, distributor, or auto parts retailer, we’re here to support your business with reliable parts and expert service.