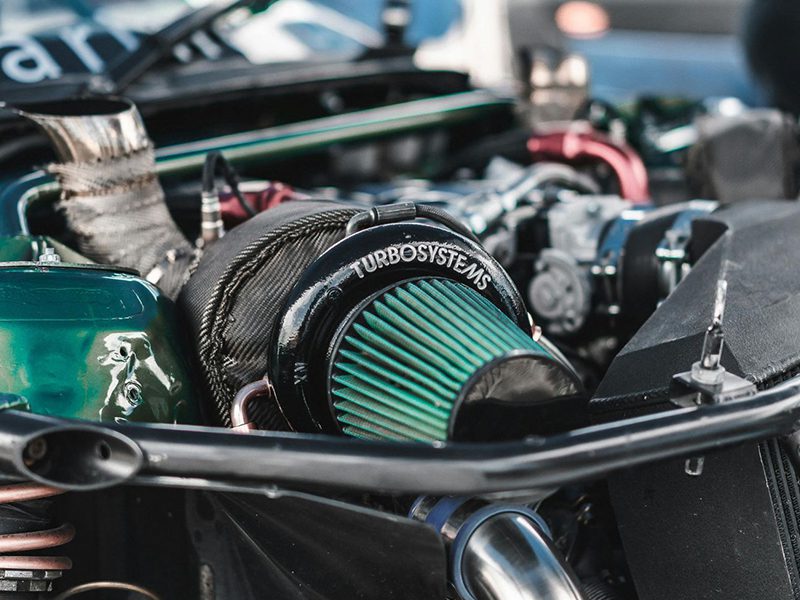
A turbocharger can add anything from 10 to 60% horsepower into a car engine. However how much horsepower a turbo adds to your car engine depends on several factors like turbocharger type, turbocharger size, boost pressure, exhaust flow and turbocharger efficiency.
The other parameters of the engine like fuel system, intake manifold, and compression ratio should also be optimized to add maximum additional horsepower. Our guide is all about answering the question, how much horsepower does a turbocharger add? in complete detail.

Understanding Turbochargers and Horsepower Gain
Each car engine is designed and developed to deliver specific horsepower. The engine displacement, rpm, air fuel ratio, and compression ratio needs to be optimized to deliver the best combination of horsepower and enough fuel efficiency, according to Provide Cars.
Now if you wish to have more horsepower in your car than the factory provided HP then one of the ways of getting that is by installing a turbocharger in your car.
Turbocharger in its simplest form is a force induction system that works to compress and deliver more air to the engine. This makes the car fuel delivery system to deliver more fuel and thus increasing the engine horsepower.
However it’s not this simple that you install a turbocharger, and you get a 60% increase in horsepower. There are several factories associated with both turbocharger and car engine that will define how much does a turbocharger add horsepower, especially at higher boost levels .
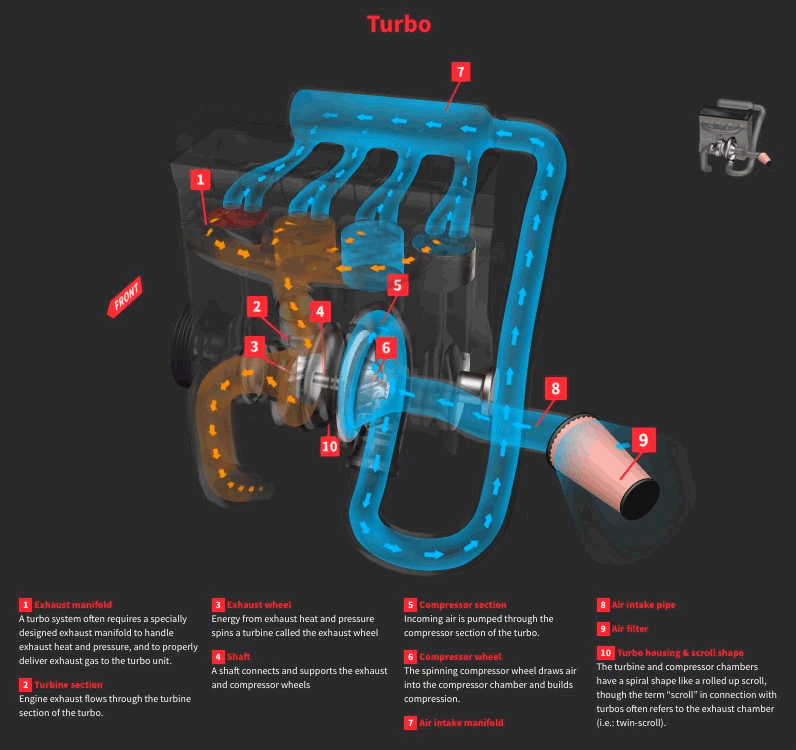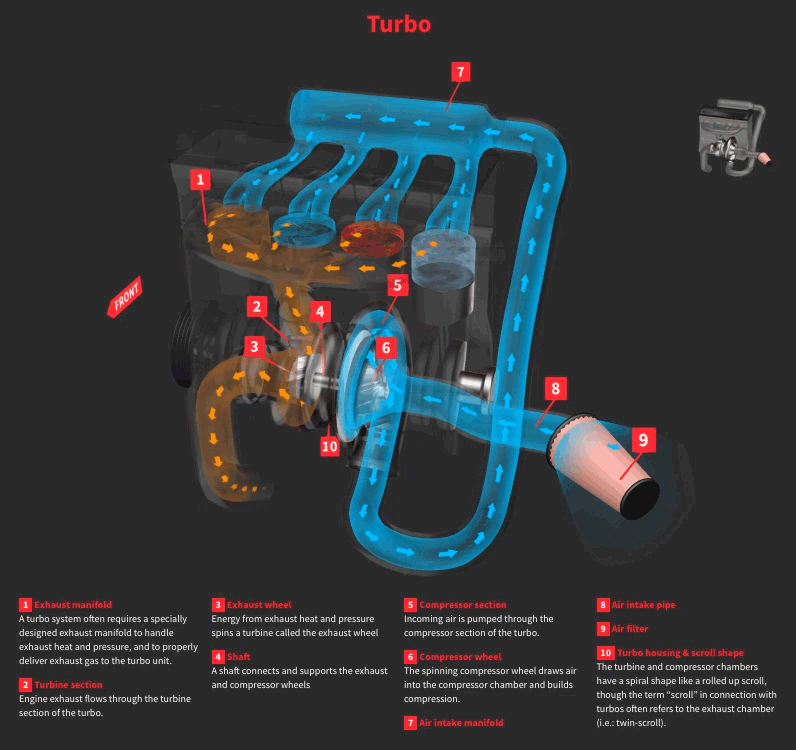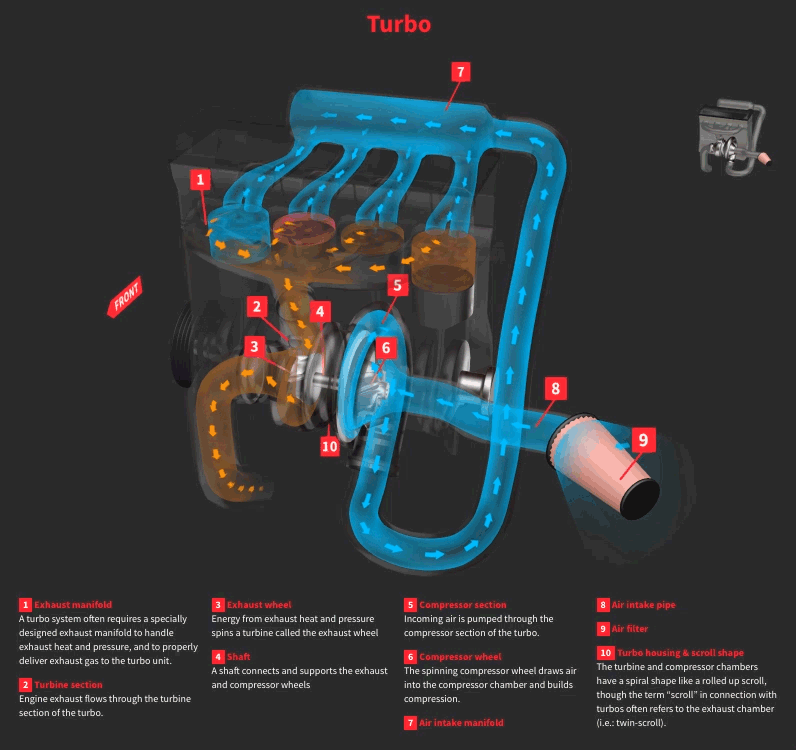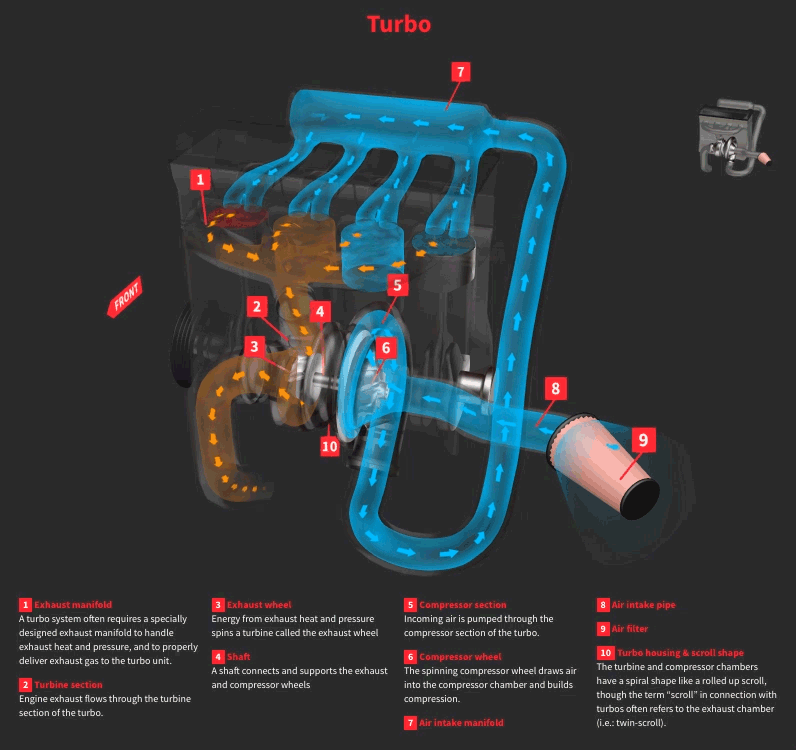
Factors Affecting Horsepower Gain
How much hp will a turbo add depends on 9 different factors associated with the car turbocharged engine, the turbocharger itself, and the weight of the vehicle. You need to perform proper engine tuning and all necessary modifications to support a specific turbocharger.
Following are factors that define how much horsepower can a turbo add.
- Turbocharger Size and Type
- Boost Pressure
- Fuel System Capacity
- Intercooling Efficiency
- Engine Management and Tuning
- Engine Internal Strength
- Exhaust System Design
- Air Intake System
- Engine Compression Ratio
Turbocharger Design and Horsepower
There are several types of turbocharger available in the market. Most common are single turbo, twin turbo, and VGT (Variable Geometry Turbo). They are also categorized as small and large size turbos. Each turbocharger design, type, and size has its own benefits and drawbacks.
Single and small turbos have less lag but offer limited boost. The twin and large turbo offer maximum HP gain but usually have slower spool. Selection of turbocharger also depends on your car engine size and capabilities.

Boost Pressure and Its Impact
Turbocharger boost is the pressure of air entering the turbocharged engine above the atmospheric pressure. As turbocharger forces more air into the engine than it usually has in natural aspire case, this increases pressure in intake manifolds.
In simpler terms, more boost a turbo develops, more air inflow will be there and higher will be the power. In detail, you need to consider the compressor map of the charger.
It explains how turbo performs at different airflows. You should be looking for an efficiency island, spot in the compressor map where turbo operates at its maximum efficiency.

You also need to consider the A/R ratio (area/radius radio) of the turbocharger. Higher the ratio, more will be the boost and higher will be the power output. However this will also result in greater turbo lag. Opposite is the case of lower A/R ratio.
There is a limit of maximum boost you can have for any specific engine. Excessive boost pressure can lead to engine knocking, overheating, loss of power output, reduced efficiency, and mechanical failure in the worst case scenario.
Intercooling and Engine Performance
Intercooling is crucial for high engine performance when running with a turbocharger. Following are some important points to consider for engine performance.
- Air heats up when compressed by the turbocharger. Heated air reduces the engine performance, so an intercooler is required.
- It cools the air fuel mixture before it enters the engine. This increases mixture density and oxygen content resulting in increased horsepower ou.
- Too much cooling of air will also affect engine performance, so the intercooler should be compatible with turbocharger and engine.

Fuel System Capacity
How much hp does a turbo add also depends on your car fuel injection system capacity and fuel flow capabilities. This is because turbocharging only adds extra air to the engine. This extra air cannot do any increase on HP until extra fuel is added into the air to keep an optimal air fuel ratio for the engine.
The car fuel injection system consists of a fuel pump, fuel lines, and fuel injectors. The car size of car fuel lines and capacity of car fuel pump and injectors should be enough to supply the engine with increased fuel needed due to the installed turbocharger.
Almost all turbochargers came with predefined fuel supply requirements to make things easy for mechanics who are installing them.

Proper Tuning for Maximum Power Gains
When you install any specific turbocharger on your car engine, you need to perform proper engine tuning aka ECU tuning.
Proper ECU tuning is needed to manage increase in following parameters due to introduction of turbocharger.
- Airflow
- Air Pressure
- Combustion conditions

The tuning will help us controls all major engine functions, including:
- Ignition timing
- Air fuel ratio
- Boost control
Ignition Timing
We need to adjust and optimize the ignition timing of the engine because when boosted, the air fuel mixture burns faster due to high pressure. This can induce knocking in the engine and result in permanent damage to engine internal parts. To prevent this the spark is adjusted to be fired later than normal position of crankshaft.
Air Fuel Ratio
Normal air fuel mixture cannot deliver more power even with a turbocharger. You need to have a rich air fuel mixture to get increased power from the engine. Ideal AFR under boost is usually 11.5 to 12.0:1 which is richer than the standard stoichiometric 14.7:1 ratio.
Boost Control
Depending on the throttle position, the engine may or may not need turbo boost. So, to manage this, the engine ECU has boost control solenoid which works to either forward or waste the boost pressure developed by turbocharger.
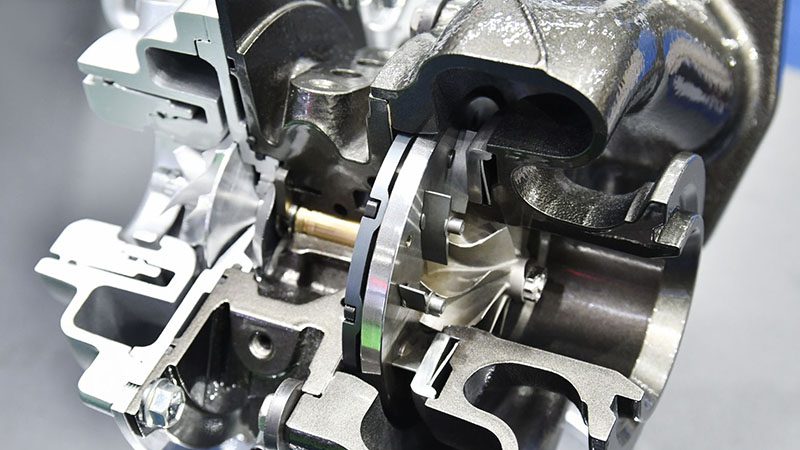
Engine Internal Strength
When turbocharger increases air pressure, that pressure along with more powerful combustion inside the engine combustion chamber, increases stress on all associated parts of the engine. Engine piston, connecting rod, cylinder head, inlet and outlet values, piston rings all face elevated pressure. All those associated parts should be able to resist that high stress to prevent mechanical failure.
Exhaust Flow and Turbocharger Efficiency
The turbocharger relies on the exhaust flow to operate and compress air. So an efficient exhaust flow mechanism will definitely improve the turbocharger efficiency. Any issue like leakage or restriction in the system can result in loss of power.
A free flowing exhaust and turbo manifold reduce back pressure and allow the turbo to operate more efficiently. So, to get the maximum out of exhaust gasses, the exhaust diameter, catalytic converter and muffler design all needs to be optimized as per the turbocharger requirements.

Air Intake System
A turbocharger does add extra air in the system but it does not have a separate air intake system to add that extra air into the engine. It forces air through the same natural aspire air intake system to make it reach the engine.
So the engine air intake system should be large and strong enough to process and resist high pressure extra air moving into the engine at optimal speed.

Engine Compression Ratio
The engine compression ratio plays a very crucial role when you are working with turbocharger horsepower increase. A higher ratio compresses air fuel mixture more and can deliver more power from the same engine.
However, the turbocharger boost pressure is considered, the air fuel mixture is already compressor. Any further compressor can result in loss of power and engine knocking or even mechanical failure.
So lowering the engine ratio based on the turbocharger boost pressure will increase the engine performance and add more horsepower to the car. You can do any one or combination of any of the following three methods to reduce ratio.
- Replacing regular pistons with specially forged low compression pistons
- By replacing your normal engine head gasket with a thicker head gasket
- Slightly enlarging combustion chamber volume by using thinner thickness cylinder sleeves
An ideal CR for turbo builds usually ranges between 8.0:1 to 9.5:1, depending on fuel quality and boost level.

Turbo Lag and Power Band Matching
Turbo lag is the duration or time gap between you putting foot on throttle and turbocharger providing you full boost. Every turbocharger has this lag as it relies on the exhaust gasses to operate.
Power band is the range of your engine rpm where it delivers the most power. So you need to match this turbo lag with the power band.
Real World Examples of Turbochargers Adding Horsepower
Based on the turbo lag and power band matching, some of the real word cases where engine horsepower was increased using a turbocharger.
| Vehicle | Engine Type | Stock HP | Turbocharged HP | Horsepower Gain | Notes | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mazda Miata (ND) | 2.0L NA I4 | 155 HP | ~248 HP (BBR turbo kit) | 93 HP | Turbo kit includes ECU tuning, intercooler, and injectors | MotorTrend |
| Subaru WRX STI (2019) | 2.5L Turbo H4 | 310 HP | ~400–450 HP (with bolt-ons and tune) | 90–140 HP | Gains achieved with larger turbo, intake, intercooler, and tune | Reddit Discussion |
| Toyota 86 / Subaru BRZ (Turbo Kit) | 2.0L NA H4 | 200 HP | ~300–350 HP | 100–150 HP | Aftermarket turbo kits from Greddy, HKS, etc., with tuning | Speedhunters |
| Nissan GT-R R35 | 3.8L Twin-Turbo V6 | ~565 HP (stock) | Twin-Turbo | 700+ HP | Standard or Add-on options based on your region | Nissan USA |
Conclusion
There is not one single or fixed number answer for how much horsepower does a turbocharger add. It depends on nine different factors associated with the car engine and turbocharger itself.
Each turbocharger has its own importance and effect on horsepower added. If you work with a few of the above mentioned nine factors you can add anything from 10% to 25% more horsepower to your car engine.
However if you work on all nine factors you can add up to 60% more horsepower into your car engine.
Follow Up
By choosing the right turbocharger and optimizing engine components, the gains in horsepower are not just theoretical – they’re achievable.

At Nanjing Woda Auto Technology Co., Ltd., we specialize in providing top-tier OEM and aftermarket automotive engine parts, including turbochargers, cylinder heads, and more.
Serving B2B customers globally, we pride ourselves on delivering high-quality solutions that power vehicles worldwide. Contact us today to discover how we can support and enhance your business.