Car mechanics and hobbyists understand the camshaft (also spelled “cam shaft”) is the unsung hero of combustion engine performance. This blog explains practically everything you need to know about camshafts.
What’s a camshaft in engine models? What’s the camshaft function? How many parts of a camshaft are there?
This piece will cover everything from a camshaft’s working to maintenance.
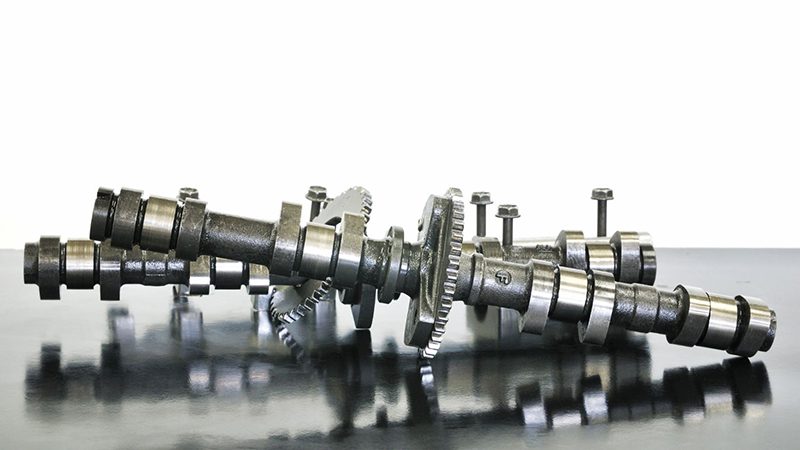

What is a Camshaft? The Unsung Hero of Car Engine Performance
Every four-stroke engine has one or two of these precision-engineered components. A camshaft opens and closes the intake and exhaust valves so the air-fuel mixture can enter and exit its combustion chambers. Some current combustion engines can even have two of these.
Camshafts have cam lobes that push against valve lifters (called “followers”). That’s how it will optimize engine performance via its rotational motion in a four-stroke internal combustion engine.
Camshaft Location and Functionality
Modern engines have camshafts located on top of the engine’s cylinders, especially the ones using an overhead cam (OHC) configuration. OHC designs make valve timing more precise so the engine can perform at higher RPMs.
However, this aggressive performance often leads to fuel inefficiency, so modern engines have variable valve timing (VVT) systems to adjust the timing of the camshaft based on the automobile’s driving conditions.

How Does a Camshaft Even Work? Cam’s Functionality Inspected
You may wonder, “What is camshaft on a car actually for?” The camshaft function is simple: It closes and opens the engine’s valves with its egg-shaped lobes (also called “cams,” hence the name camshaft); camshafts rotate and this rotation motion makes the valves move up and down so the air-fuel mixture could easily move in and out of combustion chambers.
Camshafts make sure that the intake and exhaust valves are open at certain intervals during the four-stroke cycle (intake, compression, power, and exhaust).
Camshaft Functioning: Why Is It So Important For Engine’s Performance
This is how a camshaft regulates not only the quantity of air-fuel mixtures entering the cylinder but also the timing of exhaust gases. It’ll synchronize the timing and duration of valve openings to achieve optimal combustion.
As explained above, modern VVT-enabled engines adjust the timing of valve opening based on the speed of the engine and current load conditions.
One can say that a camshaft’s efficiency affects the engine’s performance; more specifically, its power output and emissions. By ensuring that exhaust valves open and close at the right times, these shafts allow for maximum airflow during combustion cycles.
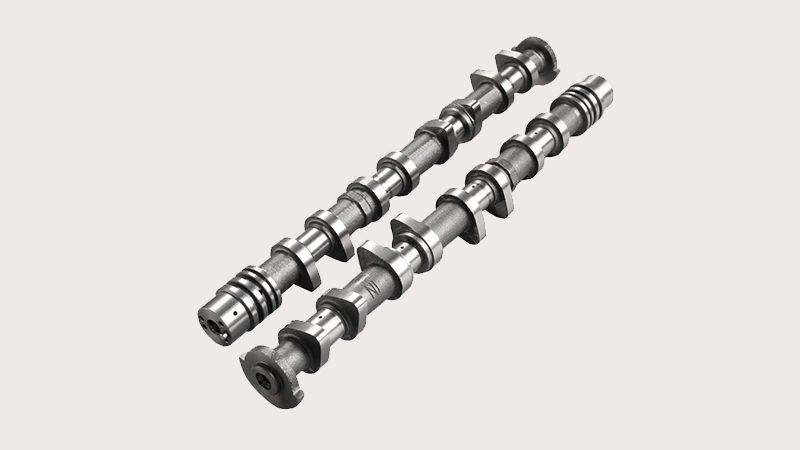

Different Parts of a Camshaft: Your Car Cam’s Full Anatomy
Camshaft Lobes
These lobes determine the timing and duration of valve openings. Each lobe comes with a set profile dictating how quickly (duration) and how far (lift) a valve stays open as the cam rotates. Lobes regulate airflow into the combustion chambers this way.
Camshaft Bearings
Bearings support camshafts by reducing friction between shafts and the cylinder head. That’s how the shaft can rotate smoothly. Bearings also determine the cam’s alignment and stability. It slows down the process of wear and tear on the camshaft.
Timing Gear
Timing chains (or belts) drive the camshaft (or some cams have gears connecting them to the crankshaft). This timing belt syncs the cam’s rotation with one of the crankshafts). So, exhaust valves open and close at the precise moment without any significant delay.
When the combustion engine starts, the crankshaft begins rotating and driving the timing mechanism that turns the cam simultaneously.

Miscellaneous
Other components of an engine camshaft include thrust washers (they control the cam’s axial motion) and cam camps (keep the shaft in place within its chassis or the engine block).
There’s also a sensor for camshafts but we’ll discuss it in another section at the end of this blog.
Not All Camshafts Are Made the Same: Exploring 4 Major Types
Driving a camshaft car is the norm nowadays. But did you know how many different types of cams are there? We’ll discuss four major camshaft types here very briefly:
Flat Tappet Cams
Flat tappet cams are widely used and feature a flat surface with lifters, also known as tappets. So, they’re very simple in design and don’t cost a lot. But they are quite high-maintenance and their lifters may get worn out over time very easily.
Older automobiles use flat tappet cams and even modern engines with less aggressive valve lift profiles utilize them.
Roller Cams
As their name indicates, roller cams have roller bearings on cam lobes. These bearings reduce friction and make roller camshafts less high-maintenance than flat tappet designs. Roller shafts can tolerate higher valve lifts and RPMs.
That’s why high-performance engines use them. But these designs can be expensive given their durability and efficiency. Performance enthusiasts prefer roller cams over flat tappet shafts.
Cast Iron Cams
Older engines used cast iron cams because of how budget-friendly and durable this material is! You won’t see many modern engines using cast iron camshafts today. That’s because modern engines favor lighter materials like steel/aluminum over cast iron.
That’s why cast iron designs have gone out of style.
Steel Billet Cams
However, the outmoded cast iron cams were replaced by steel billet designs, used frequently in high-performance engines where speed is necessary. These camshafts are machined from solid steel billets for customized profiles that greatly enhance engine performance.
These designs are popular in Formula 1 racing where optimized valve timing and lift give drivers substantial gains in horsepower and torque.

How Do They Make It? Camshaft Manufacturing Explained
Car manufacturers use different metals when constructing engine camshaft designs. Vehicular manufacturers focus on the material’s durability and performance characteristics.
For instance, these materials in camshaft construction:
- Hardenable Iron: Iron that can be hardened under pressure substitutes steel camshafts in the construction process because it’s robust, durable, and friction-resistant.
- Chilled Chrome Cast Iron: This material plays a key role in the casting process since it lets manufacturers strike a balance between strength, toughness, and flexibility.
- Carbon Steel (EN8/EN9): Manufacturers use carbon steel for roller and hardened cams due to its strength and toughness. En8 steel has a carbon content of up to 0.50% while En9 steel has a carbon content of up to 0.60%.
- Nitriding Steel (En40B): Also called 722M24, this chromium-molybdenum alloy is the best option for manufacturing camshafts because it features a hard surface finish along with lightweight properties. Manufacturers prefer it for its A1 performance and long life.

Timing Belt And Its Peculiar Effect on Camshaft Performance
When discussing the components of a camshaft, this blog discussed the timing belt or chain.
This belt or chain keeps the camshaft’s rotation in sync with the crankshaft. That’s how cam lobes work in unison with the moving piston.
The camshaft moves at 0.5x the speed of the crankshaft. The belt connects these two and holds them together. So, the timing chain achieves the precise valve timing required for the engine’s optimal performance during the engine cycle (the four strokes).
If the timing belt fails or becomes faulty, it disrupts this synchronization; in that case, the camshaft malfunctions and degrades the engine’s performance.

Why Do You Need a Well-Functioning Cam? Exploring the Benefits
It should be clear to you at this point why a camshaft car needs this crucial component.
Here are the key benefits of a well-functioning camshaft to help you better understand why a faulty cam hinders your engine’s performance:
- Cams keep engines at their optimal performance and make sure that an engine is delivering max power.
- Camshafts regulate the timing and duration of valve opening and closing to optimize fuel economy.
- A camshaft enhances combustion efficiency to lower emissions and gives car owners a cleaner running engine.
- A cam will minimize stress on other engine components like valve springs & lifters; so, your engine’s lifespan extends because of the cam.

Cam Troubleshooting 101: 5 Common Issues Explained
- Insufficient Lubrication: Since the camshaft relies on a thin oil film to reduce friction, overheating can diminish lubrication and lead to wear & tear.
- Faulty Installation: Worn or mismatched components can cause premature wear in a cam, especially when the manufacturer doesn’t install it properly.
- Mechanical Interference: Moving parts constantly hitting each other can lead to cracks or fractures in your car’s camshaft.
- Improper Break-In: New cams rely on a break-in procedure for developing particular wear patterns. When the break-in goes wrong, the cam starts malfunctioning.
- Material Fatigue: Constant stress and heat exposure can lead to material fatigue so the cam may start cracking or losing its robust shape.

Is Your Camshaft Faulty? 7 Signs That Scream ‘Yes’
- The Check Engine light turning on is often the first sign that the cam is malfunctioning.
- When your engine feels unsteady while driving, it may be due to a malfunctioning cam.
- A faulty camshaft prevents an engine from maintaining its speed or responding to throttle inputs right away.
- Increased fuel consumption or poor fuel efficiency might also indicate a faulty cam.
- Noisy tapping sounds or ticking noises are another telltale sign.
- If you see metal debris during an oil change, book an appointment with your mechanic.
- A faulty cam can cause one or more cylinders to misfire due to improper valve timing.
Peak Performance Unlocked: 6 Camshaft Maintenance Tips
- Keep a clean engine and replace your air filters.
- Use quality engine oil for sufficient engine lubrication.
- Check your timing chains for signs of wear, cracks, or stretching.
- Address issues like rough idling or reduced power right away.
- Never push your engine beyond its recommended RPM limits, please.
- Adhere to your vehicle manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines for camshaft care.

Camshaft Position Sensor: What Is It And What Does It Do?
As promised, this blog will now discuss an often-neglected component that comes with cams, i.e., camshaft position sensors. Most modern engines will have this sensor so it can monitor the cam’s velocity and position.
Let’s look into the functioning and value of the camshaft sensor.
Whereabouts
The sensor is located near the camshaft or valve cover on the engine. But different makes and models will have different locations for this sensor.
Working
The camshaft sensor provides essential data to the engine control unit (ECU). That’s how it can adjust fuel injection timing and ignition timing based on the camshaft’s position.
Complications
A malfunctioning camshaft position sensor leads to issues like rough idling, misfires, power reduction, and poor fuel efficiency. If the sensor fails, it triggers the Check Engine light and generates diagnostic trouble codes related to camshaft timing.
Replacement
If a fault is detected in the camshaft position sensor, it may need to be replaced to restore proper engine function. Replacing this sensor is generally a straightforward process, but the vehicle owner must ensure that the new sensor is compatible with the vehicle’s specifications.

Final Remarks: What’s Next For You?
This blog explains that the camshaft rotates to cause the up-and-down motion for the engine’s valves during the intake and exhaust process and regulate the flow of air-fuel mixtures into and out of the system. That’s why you should invest in a quality car engine camshaft to keep your engine’s performance at max.
If your cam shows signs of extreme wear and tear, then you may consider replacing it for good. That’s when you need the help of a company with ample experience in automotive parts.
Nanjing Woda Auto Technology Co., Ltd. has been a trusted name in the automotive engine parts industry since 1999. With 25 years of experience, we specialize in the distribution of high-quality, long-life engine components.

We offer a product catalog of over 100,000 SKUs and export to more than 100 countries and regions—including Europe, North and South America, Africa, and the Middle East. Our commitment to quality, reliability, and global support makes us a preferred partner for wholesalers, distributors, and automotive service providers worldwide.
Contact us today to source dependable camshaft replacements and other essential aftermarket engine parts tailored to your market needs.





