When it comes to engine performance, efficiency, and driving dynamics, engine configuration plays a critical role. Whether you’re an automotive enthusiast, a reseller, or a fleet operator, understanding the key differences between V-type and inline engines is essential for making informed, strategic decisions.
These two engine layouts each offer distinct advantages and trade-offs that affect packaging, maintenance, power delivery, and fuel economy. The inline vs. V engine debate remains one of the most important considerations in both vehicle design and engine sourcing.
In this guide, we’ll explore how each configuration works, where they perform best, and how to determine which layout is best suited to your needs or those of your customers.

Understanding Inline Engines
Inline engines (also called straight engines) have all their cylinders arranged in a single row. Common examples include inline-4 (I4) and inline-6 (I6) engines. This configuration is known for its simplicity, balance, and fuel efficiency.
Key Benefits of Inline Engines:
- Simple Design: Easier to manufacture and maintain due to fewer components.
- Fuel Efficient: Typically uses less fuel than a V-type engine of the same displacement.
- Smooth Operation: Especially true for inline-6 engines, which are naturally balanced.
- Lower Cost: Fewer parts and a compact structure often result in lower repair and production costs.
Limitations:
- Limited Power Output: Inline-4 engines are often less powerful than similarly sized V6 or V8 engines.
- Space Constraints: Longer design can be harder to fit in smaller engine bays, especially in rear-wheel drive layouts.
Best for: Everyday vehicles, front-wheel drive cars, and compact cars where efficiency and affordability are top priorities.

V Engine Design and Benefits
V-type engines have two banks of cylinders arranged in a “V” shape, typically set at a 60- to 90-degree angle. Popular formats include V6, V8, and even V12 configurations.
Key Benefits of V Engines:
- More Power: Can accommodate more cylinders, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
- Compact Length: Shorter than inline engines, making them easier to fit in various vehicles.
- Better Weight Distribution: Allows for a lower center of gravity and improved balance in sports or luxury cars.
- Smooth Acceleration: Quick throttle response and higher torque are common characteristics.
Limitations:
- Complex Design: More components mean more parts that can wear out or fail.
- Higher Maintenance Cost: Repairs can be more time-consuming and expensive.
- Heavier Engine Block: Increased weight can reduce fuel efficiency.
Best for: Sports cars, luxury vehicles, trucks, and applications where power and performance are more important than economy.
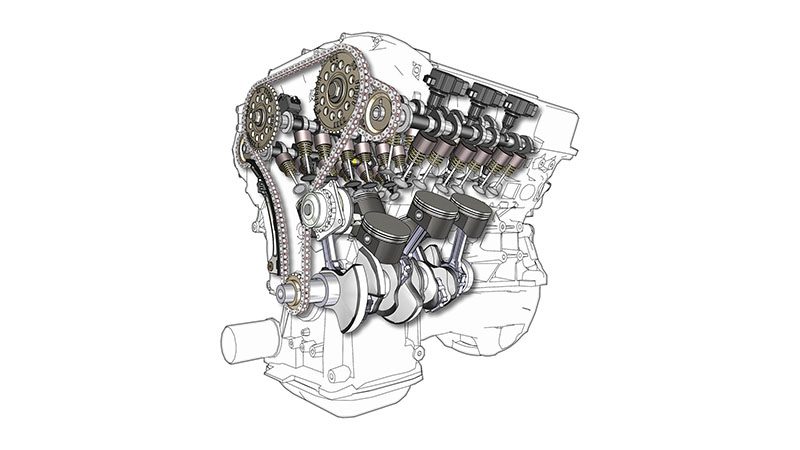
Inline vs V Engine: Side-by-Side Performance Comparison
| Feature | Inline Engine | V-Type Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Simplicity High – All cylinders are aligned in a single row, resulting in a straightforward design with fewer components. Easier to manufacture and maintain. | Moderate – Two cylinder banks arranged in a "V" shape require more complex engineering, including additional components like dual cylinder heads and extra camshafts. |
| Fuel Efficiency | Better in most cases – Inline engines typically weigh less and have fewer moving parts, which reduces friction and improves fuel economy. | Slightly lower – The added weight, complexity, and increased internal friction in V engines often result in reduced fuel efficiency, especially in larger V6 or V8s. |
| Power Output | Moderate – Inline-4 engines are great for daily driving but limited in horsepower and torque. Inline-6s offer better performance but take up more space. | Higher – V6, V8, and larger V engines deliver greater horsepower and torque, making them ideal for sports cars, performance vehicles, and trucks. |
| Engine Balance | Excellent in I6 engines – Inline-6 engines are naturally balanced and offer incredibly smooth operation. Inline-4s are decent with balance shafts. | Good with balancing shafts – V engines are not inherently balanced, especially at certain cylinder counts, but use balance shafts or crank offsets to improve smoothness. |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing and repair costs – Fewer parts and easier access make inline engines cheaper to build and maintain. | Higher cost due to complexity – More parts, tighter packaging, and dual components (like heads and cams) result in increased production and service costs. |
| Packaging | Longer but narrower – The linear layout can be harder to fit transversely in compact engine bays but offers excellent access for repairs. | Shorter and wider – The V configuration reduces engine length, making it easier to fit in a variety of engine bays, especially in longitudinal or RWD applications. |
| Best Use Case | Daily driving, economy cars – Ideal for compact cars, fuel-efficient sedans, and vehicles where reliability and cost matter most. | Performance, luxury, towing – Common in high-end sedans, SUVs, muscle cars, and trucks where power, torque, and refinement are essential. |
Handling and Stability
V-type engines are commonly used in performance and luxury vehicles due to their shorter length and compact design, which allows for better engine bay packaging and a lower center of gravity. This positioning improves cornering stability, reduces body roll, and supports balanced front-to-rear weight distribution, especially in rear-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive platforms.
On the other hand, inline engines—with their long, narrow layout—are ideal for transverse mounting in front-wheel-drive vehicles. This configuration not only saves space but also contributes to predictable handling and efficient weight placement over the front axle. Inline engines, especially inline-6 variants, are also known for their natural balance and reduced vibration, resulting in a smoother ride and improved driver comfort.
However, it’s important to note that handling is a system-level outcome, influenced by more than engine layout alone. Suspension geometry, chassis rigidity, steering setup, and tire selection all work in concert with engine placement to determine how a vehicle behaves on the road.

Maintenance and Longevity
Inline Engines
Easier to maintain: With a simpler, straight-line design and fewer components—typically only one cylinder head, one camshaft set, and fewer timing components—inline engines offer better access to parts, making repairs faster and less labor-intensive.
Lower costs: Their straightforward layout leads to lower labor costs, fewer potential failure points, and cheaper replacement parts, which makes them popular for economy cars and fleet vehicles.
V-Type Engines
Potentially more durable: V engines are often engineered for higher performance and load capacity, with robust internal components designed to handle more power and stress.
Higher upkeep: However, they typically include two cylinder heads, dual exhaust manifolds, and sometimes multiple camshafts, which make diagnostics, repairs, and part replacements more complex and time-consuming. This translates to higher maintenance and service costs over time.
Regardless of engine type, routine maintenance—such as oil changes, filter replacements, coolant flushes, and timing system inspections—is critical to extending engine life and preventing costly breakdowns. Following the manufacturer’s service schedule ensures the engine stays reliable, efficient, and long-lasting.

Popular Inline and V-Type Engines in Real Cars
| Engine Type | Model | Engine Code | Cylinder Configuration | Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inline | Toyota Corolla | 2ZR-FE | I4 | Excellent fuel economy and bulletproof reliability. Widely used in compact sedans worldwide. |
| BMW 3-Series / Toyota Supra | B58 | I6 | Smooth, turbocharged inline-6 with refined power delivery. Popular among enthusiasts and luxury-performance vehicles. | |
| Honda Civic | L15 | I4 | Turbocharged variant delivers strong torque, low fuel consumption, and reliable daily performance. | |
| Ford Escape | EcoBoost 1.5L | I3/I4 | Compact turbo engine with a solid balance of efficiency and power for urban driving and compact crossovers. | |
| Hyundai Elantra / Kia Forte | Gamma 1.6L | I4 | Versatile and efficient inline-4 engine known for low maintenance and everyday drivability. | |
| V-Type | Ford F-150 | 5.0L Coyote | V8 | Naturally aspirated V8 designed for towing and durability. A key feature of Ford’s best-selling pickup truck. |
| Chevrolet Camaro / Corvette | LS3 | V8 | Classic muscle car engine offering powerful performance and tuning flexibility. | |
| Toyota Highlander / Lexus RX | 2GR-FKS | V6 | A smooth, reliable V6 used across Toyota’s midsize SUV and crossover lineup. Known for longevity and fuel efficiency. | |
| Nissan 350Z | VQ35DE | V6 | High-revving, naturally aspirated V6 with a reputation for smooth operation and durability in sporty applications. | |
| Honda Pilot / Odyssey | J35 | V6 | Delivers refined performance and strong torque in larger vehicles. Features Honda’s trusted VTEC technology. |

Which Configuration Is Right for You?
For B2B buyers—whether you’re sourcing engines for resale, fleet use, or vehicle assembly—choosing between an inline and V-type engine depends on your operational priorities and customer demands.
Choose an inline engine if your focus is on:
- Fuel efficiency and affordability — Ideal for compact cars, taxis, and budget-conscious fleets
- Ease of maintenance — Fewer components mean lower service costs and reduced downtime
- High-volume applications — Common in economy vehicles and suitable for markets prioritizing cost-effective transportation solutions
Choose a V-type engine if your business requires:
- Higher performance and torque — Preferred for pickup trucks, SUVs, and performance-oriented vehicles
- Towing capacity and power output — Especially relevant in commercial, off-road, or utility applications
- Upscale vehicle builds — A better fit for luxury and high-end vehicle platforms with demanding specs
For OEMs and distributors, engine configuration selection also depends on factors like target market trends, regulatory compliance (e.g., emissions or fuel economy standards), assembly compatibility, and regional service infrastructure.

Conclusion
Both inline and V-type engines offer compelling advantages depending on the application. Inline engines are known for their simplicity, fuel efficiency, and lower maintenance, while V-type engines stand out for their power, performance, and versatility in heavier or high-end vehicles.
Understanding these differences allows B2B buyers, fleet managers, and automotive professionals to make informed decisions—whether you’re sourcing engines for passenger cars, commercial fleets, or performance builds.
At Nanjing Woda Auto Technology Co., Ltd., we specialize in supplying high-quality brand-new auto engines and components to global B2B clients. With over 25 years of experience in the industry, we provide reliable powertrain solutions tailored to your business needs.
Need expert help choosing the right engine for your market or application?
Browse our full catalog at autopartswd.com or contact our team today to get competitive pricing, fast quotes, and professional support.