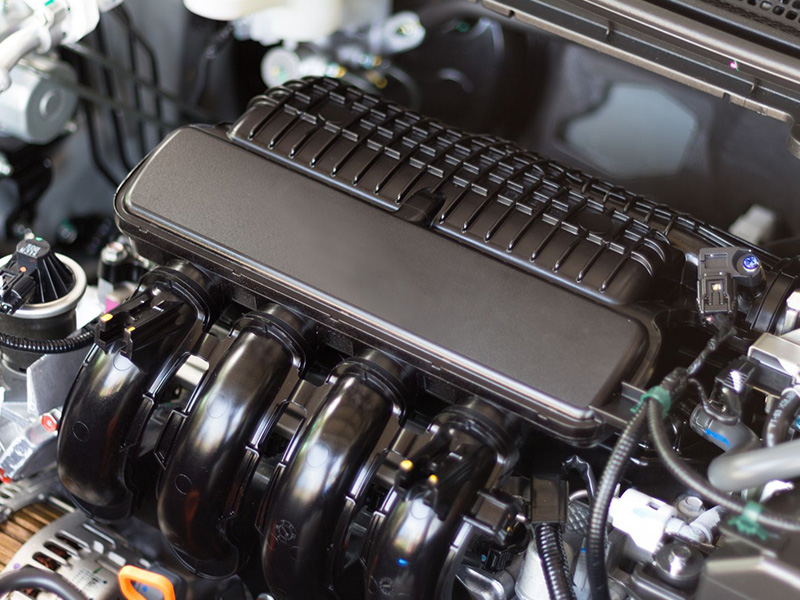
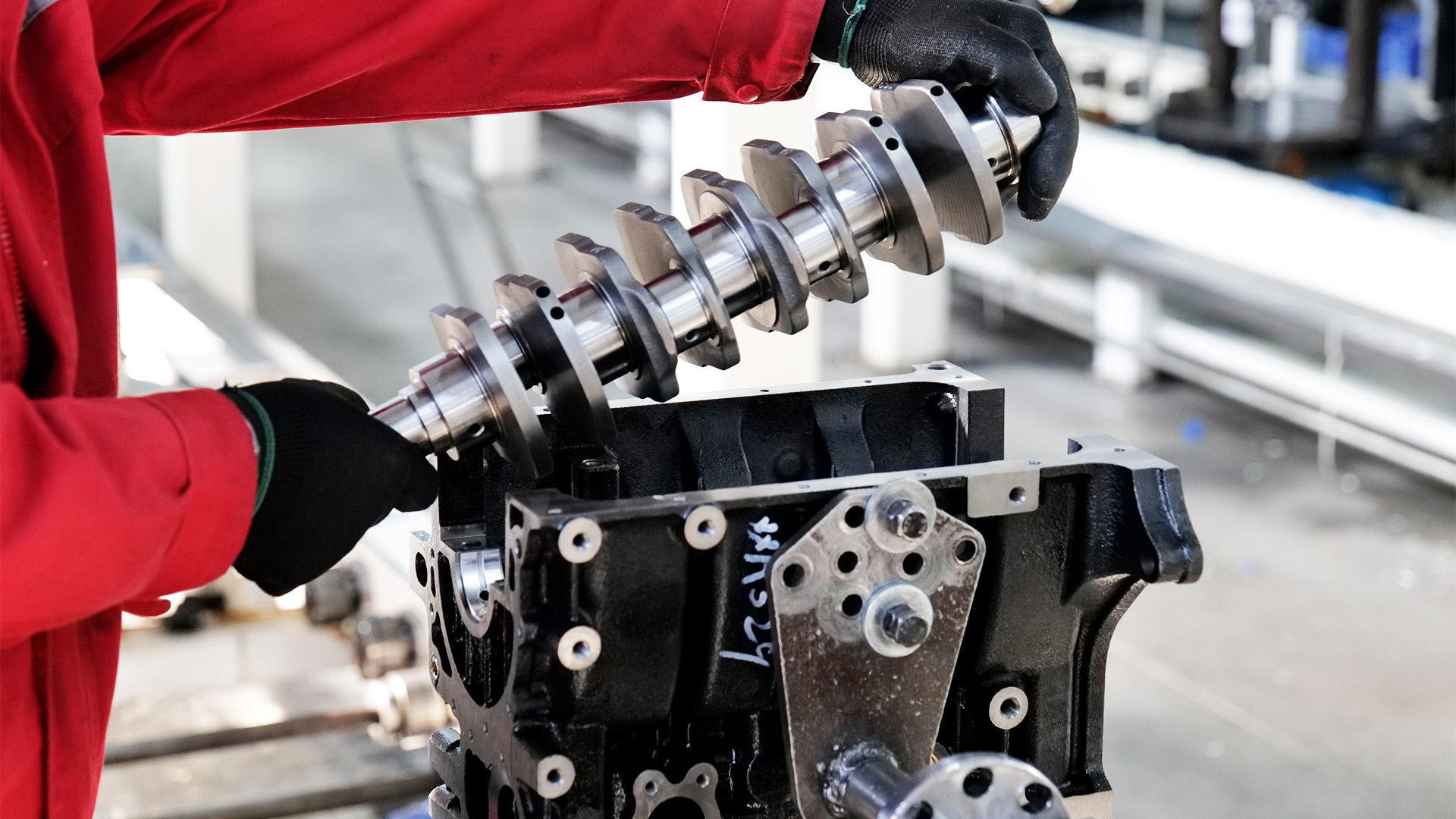
The Volkswagen TDI engine stands as one of the most successful and recognizable VW diesel engines ever built. Known for its balance of power, torque, and fuel efficiency, it has powered millions of Volkswagen vehicles worldwide — from passenger cars to commercial fleets — and remains a benchmark for modern diesel technology.
In this guide, we’ll take a closer look at the VW TDI engine’s design, key generations, reliability, and maintenance essentials. Whether you’re sourcing complete engines, rebuilding units, or maintaining them for clients, this overview will help you understand what makes the TDI a lasting name in diesel performance.
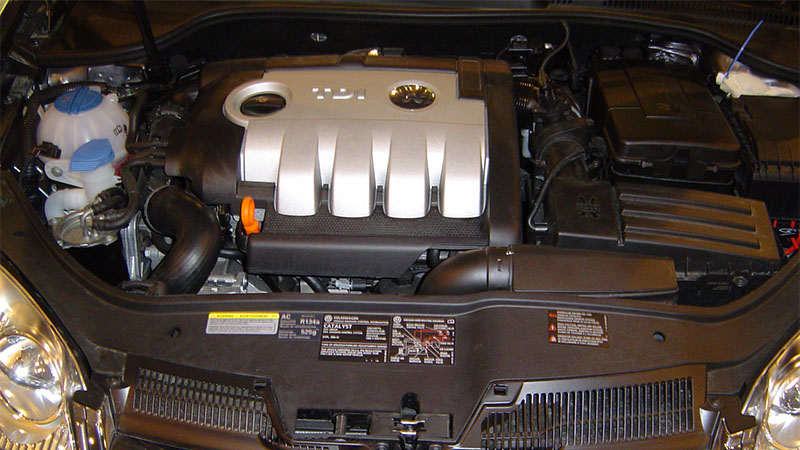

What Does “TDI” Mean?
Definition & Branding
TDI stands for Turbocharged Direct Injection. In simple terms, it’s a diesel engine that uses a turbocharger to increase air intake and direct fuel injection to deliver fuel straight into the combustion chamber — improving both efficiency and power.
There’s occasional debate about what the “D” represents — some say “Diesel,” others “Direct.” Regardless, TDI is Volkswagen Group’s signature branding for its line of turbo-diesel engines used across Volkswagen, Audi, SEAT, and Škoda vehicles.
How the TDI Engine Works
Here’s how it works in plain terms:
- Air is compressed inside the cylinder until it’s hot enough to ignite diesel fuel.
- A turbocharger uses exhaust gases to force more air into the engine, boosting power and efficiency.
- Direct injection delivers precisely measured diesel fuel into the combustion chamber at high pressure.
The result is a diesel engine known for strong low-end torque, impressive fuel economy, and long-distance reliability — making it a favorite for both everyday drivers and professional fleets.

Evolution of VW’s TDI Engines
Volkswagen’s TDI (Turbocharged Direct Injection) technology has evolved through several major generations since its debut in 1989 — each improving performance, efficiency, and emissions control while maintaining the brand’s reputation for diesel durability.
Early Era (1989–2000s)
Volkswagen’s first TDI engine debuted in 1989 with the Audi 100 2.5 TDI, a five-cylinder diesel that marked the beginning of VW’s modern diesel era. Soon after came the 1.9 TDI, one of Volkswagen’s most successful engines, powering models such as the Golf, Jetta, and Passat.
Renowned for its simplicity and strength, the ALH 1.9 L (1998–2003) remains highly regarded among enthusiasts for its low maintenance costs and ability to exceed 300,000 miles with proper care.

Transition & Emissions Era (2000s–2015)
As emissions standards tightened worldwide, Volkswagen advanced its diesel technology. The older Pumpe Düse (PD) unit-injector system used in the late 1990s and early 2000s was replaced by common-rail injection, which offered smoother operation and cleaner combustion.
The EA189 engine family, introduced around 2007, became the backbone of VW’s diesel lineup — improving refinement and efficiency — but was later at the center of the Dieselgate emissions scandal in 2015, which led to major recalls and stricter regulatory oversight.
Modern / Legacy TDI & Future Outlook
The EA288 generation, launched around 2012, introduced a modular platform with upgraded fuel injection, SCR (AdBlue) systems, and improved fuel economy. These engines are quieter, cleaner, and meet Euro 6 standards.
As Volkswagen pivots toward hybrid and electric vehicles, diesel engines are being gradually phased out of passenger models. Still, the TDI legacy endures — particularly in commercial, export, and high-torque applications where diesel efficiency remains unmatched.
Overview of VW TDI Engine Generations
| Generation / Era | Years Active | Engine Family / Codes | Technology Highlights | Common Models | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early Era | 1989–2000s | 2.5 L R5 TDI (1T), 1.9 TDI (1Z, AHU, ALH) | First turbo-diesel with direct injection; simple, durable design | Audi 100, Golf III–IV, Jetta IV, Passat B4–B5 | Legendary reliability; ALH 1.9 TDI often exceeds 300,000 mi |
| Pumpe Düse (PD) Era | 1998–2007 | 1.9 TDI (AHF, ASZ, ARL), 2.0 TDI (BKD) | Unit-injector system for higher pressure and power | Golf IV–V, Passat B5–B6, Audi A3 8L/8P | Strong performance but noisier; camshaft wear common |
| Common-Rail EA189 Era | 2007–2015 | EA189 (1.6 TDI, 2.0 TDI CBAA/CBAB) | Common-rail injection; smoother, quieter; DPF added; Euro 5 compliant | Golf VI, Passat B7, Jetta V–VI, Tiguan | Central to Dieselgate (2009–2015); recalls & software updates applied |
| Modern EA288 Generation | 2012–Present | EA288 (1.6 TDI, 2.0 TDI CRLB/CRMB) | Modular platform; SCR (AdBlue); lower CO₂; Euro 6 standards | Golf VII–VIII, Passat B8, Transporter T6 | Cleanest and most refined; foundation of VW’s latest diesel line |
| Future & Legacy | 2020s → | EA288 Evo / Commercial Variants | Refined diesel for select markets; optimized for commercial use | Transporter T6.1, Crafter, Amarok | VW phasing out diesel cars in some regions; legacy support continues |
Each generation of Volkswagen’s TDI engines reflects the company’s ongoing response to tighter emission rules and evolving market demands. From the durable 1.9 TDI that built VW’s diesel reputation to the cleaner, more advanced EA288, the TDI story is one of continual refinement — proving that, with proper maintenance, these engines can deliver outstanding performance and longevity across decades.
Key Benefits of VW TDI Engines
Volkswagen’s TDI engines have earned their reputation for combining strong performance with exceptional efficiency and reliability. Designed for long-distance driving and demanding use, they remain a favorite among both drivers and fleet operators.
- Strong Low-End Torque:
Turbocharging and direct injection deliver peak torque between 1,500–2,500 RPM, providing excellent pulling power for towing, heavy loads, or highway cruising without needing high revs. - Excellent Fuel Economy:
TDI engines are 15–25% more fuel-efficient than comparable gasoline engines. For long trips or fleet use, that means lower fuel costs and fewer refueling stops. - Long Driving Range:
Efficient combustion and larger fuel tanks allow many TDI models to exceed 600–700 miles per tank, making them ideal for highway or cross-country driving. - Proven Durability:
With proper care — regular oil changes, correct diesel grade, and timing belt maintenance — many TDI engines surpass 200,000 miles, and some reach over 300,000 in commercial use.
For high-mileage drivers and business fleets, the VW TDI engine offers an unmatched blend of torque, fuel savings, and longevity — provided it’s maintained to factory standards.

Common Issues & What to Watch Out For
Emissions & Regulatory Legacy
The Dieselgate scandal revealed that certain 2009–2015 TDI engines used software that altered emissions results during testing. While VW resolved most cases through recalls and retrofits, it’s still essential to check whether any used TDI you’re considering has received its official update.
Mechanical & Ownership-Specific Issues
All diesels require proper care, and TDIs are no exception. Common issues include:
- Clogged DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter): Short-distance driving can prevent the filter from cleaning itself properly.
- Turbocharger wear: The turbo works hard and can fail if oil changes are neglected.
- Fuel injector problems: Especially in early common-rail engines.
- Carbon buildup: Caused by exhaust gas recirculation and short trips.
- Timing belt maintenance: Must be replaced on schedule to prevent engine damage.
These engines thrive on regular servicing and consistent highway driving. City use, infrequent oil changes, or the wrong oil can all lead to trouble.

Buying a Used VW TDI – Inspection Tips
If you’re considering a used TDI, here’s a quick checklist:
- Verify the engine code (ALH, PD, EA189, etc.) and research its track record.
- Review the service history — especially timing belt, DPF, and injector maintenance.
- Confirm whether emissions updates have been applied.
- Avoid cars with aftermarket DPF/EGR deletes unless you understand the legal and mechanical consequences.
- Consider how the car was driven — long trips are ideal; constant short trips can be a red flag.

Reliability, Lifespan & Cost of Ownership
A well-maintained VW TDI engine can often exceed 200,000 miles, and some units have been known to reach 300,000 miles or more when serviced properly. Its durable design, efficient combustion, and strong internal components make it one of VW’s longest-lasting engine families. However, longevity depends heavily on correct oil use, regular timing belt and water pump replacement, and proper DPF and EGR maintenance.
Compared with gasoline engines, TDI models typically cost more upfront and have pricier components — such as injectors, turbos, and emission systems. Yet for high-mileage drivers or fleet operators, their superior fuel efficiency and extended service life often outweigh the higher maintenance costs.
As diesel regulations tighten and new models phase out the technology, resale value and parts availability will increasingly vary by region. Markets with strong diesel demand may continue to offer solid returns, while others shift toward hybrid and electric powertrains. Before investing or stocking TDI units, it’s wise to assess local trends and long-term service support.

Should You Buy a VW TDI?
The Volkswagen TDI engine remains one of the most popular diesel options among workshops, importers, and fleet managers. It offers exceptional torque and fuel efficiency, but it’s not ideal for every operating environment. Here’s a quick comparison to help you decide whether it’s the right choice for your business.
VW TDI Engine: Pros & Cons for B-End Customers
| Category | Advantages | Considerations / Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Performance & Power | High torque output at low RPM; ideal for towing, cargo, and highway driving | Not designed for frequent short trips or stop-and-go traffic |
| Fuel Efficiency | 15–25% better fuel economy than comparable gasoline engines | Diesel fuel cost and availability vary by region |
| Durability & Lifespan | Proven reliability; many engines exceed 200,000–300,000 miles with proper care | Requires strict adherence to maintenance intervals |
| Operating Costs | Lower long-term fuel expenses and extended service intervals | Higher part costs (injectors, turbo, DPF, EGR) can raise repair bills |
| Fleet Value / ROI | Excellent for fleets or distributors serving long-distance or export markets | Resale value affected by diesel regulations in some cities/countries |
| Service & Support | Wide global availability of components and rebuild kits | Needs trained technicians for modern common-rail systems |
Buyer’s Checklist for Workshops & Distributors
- Assess usage: Best for highway, cargo, and long-route vehicles. Avoid heavy urban stop-and-go cycles.
- Verify compliance: Ensure all emission recalls or software updates are completed.
- Confirm engine code: Choose reliable series such as the 1.9 TDI (ALH) or EA288 with known service history.
- Plan maintenance budget: Include costs for timing belt, DPF, turbo, and injector servicing.
- Evaluate your market: Check local fuel prices, emission rules, and demand before bulk purchasing or import.
Bottom Line:
For B2B buyers focused on performance, fuel economy, and long-term reliability, the VW TDI remains a dependable investment. When used in the right conditions and serviced correctly, it offers excellent returns and customer satisfaction. However, in markets moving quickly toward hybrid or electric platforms, distributors should balance diesel inventory with future demand trends.

FAQ
What’s the difference between TDI and SDI?
SDI stands for Suction Diesel Injection — a non-turbo version of VW’s older diesel engines. TDI includes a turbocharger, giving more power and better performance.
Is the VW TDI engine reliable?
Yes, when maintained properly. Simpler versions like the 1.9 TDI are particularly well-regarded. Reliability depends on servicing, fuel quality, and driving habits.
How much does it cost to maintain a VW TDI?
Routine maintenance is similar to other cars, but diesel parts (turbo, injectors, DPF) can be costly if neglected. Staying ahead with regular service reduces risk.
Which VW TDI engine codes are most reliable?
Many owners consider the ALH 1.9 TDI (late-1990s to early-2000s) among the best. Later engines like the EA189 or EA288 can be reliable too if serviced correctly.
Are TDI engines still being made?
Yes, but mainly for select models and markets. VW has largely shifted its focus toward electrification, though diesel remains available in some regions.
Can I convert a petrol VW to a TDI?
Technically possible but impractical — the cost, wiring, and legal hurdles make it unrealistic for most drivers.

Conclusion
Volkswagen’s TDI engines have long set the benchmark for diesel performance — blending turbocharging, direct fuel injection, and outstanding fuel economy into a durable, torque-rich powertrain. From the legendary 1.9 TDI to the advanced EA288 generation, these engines have evolved through decades of innovation, earning both admiration for their reliability and scrutiny for their emissions legacy.
When properly maintained and matched to the right driving profile, a VW TDI can deliver years of dependable service with excellent efficiency and power. However, it’s not the right choice for everyone. Diesel-specific maintenance, emission-system care, and tightening regulations mean these engines perform best in the hands of professionals, fleets, or drivers who understand how to keep them running at their peak.
About Us
At Nanjing Woda Auto Technology Co., Ltd., we supply high-quality engines, long blocks, short blocks, and precision components to importers, distributors, and professional workshops worldwide. With over 25 years of manufacturing and export experience, we’re dedicated to helping our partners keep vehicles running stronger and longer.
Looking to source reliable engines or components?
Contact us today to explore our range or request a customized quotation.